Apelin-13
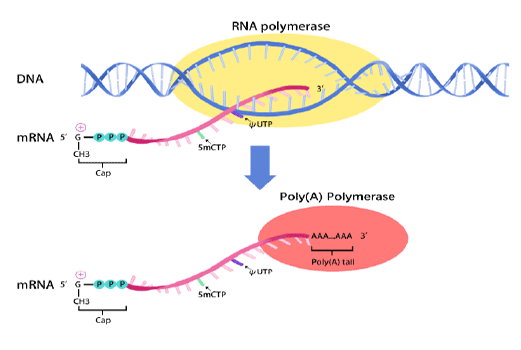
mRNA synthesis
In vitro transcription of capped mRNA with modified nucleotides and Poly(A) tail
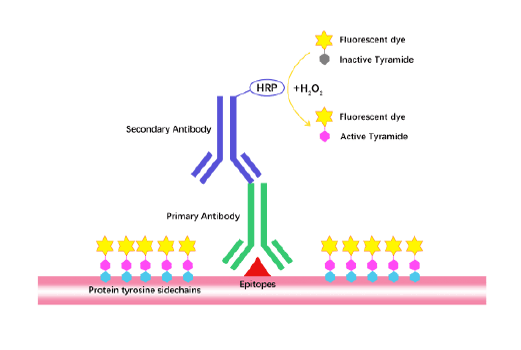
Tyramide Signal Amplification (TSA)
TSA (Tyramide Signal Amplification), used for signal amplification of ISH, IHC and IC etc.
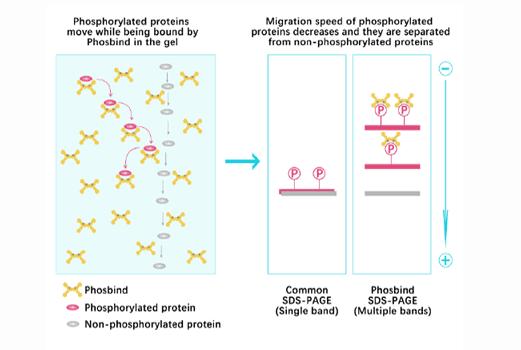
Phos Binding Reagent Acrylamide
Separation of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated proteins without phospho-specific antibody
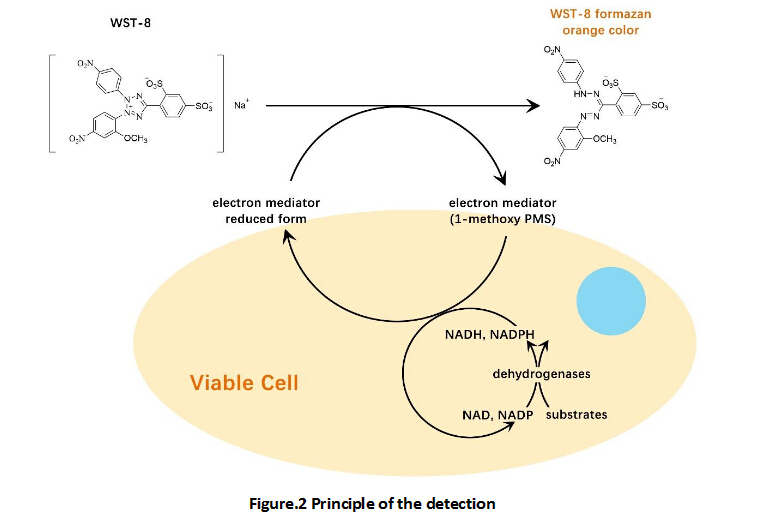
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
A convenient and sensitive way for cell proliferation assay and cytotoxicity assay
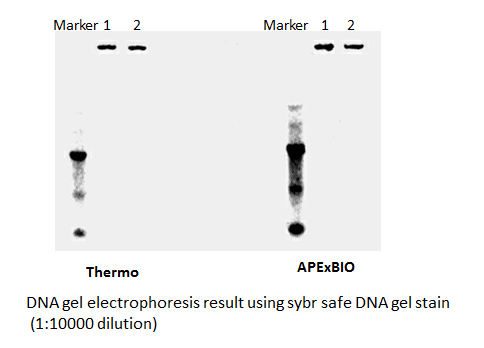
SYBR Safe DNA Gel Stain
Safe and sensitive stain for visualization of DNA or RNA in agarose or acrylamide gels.
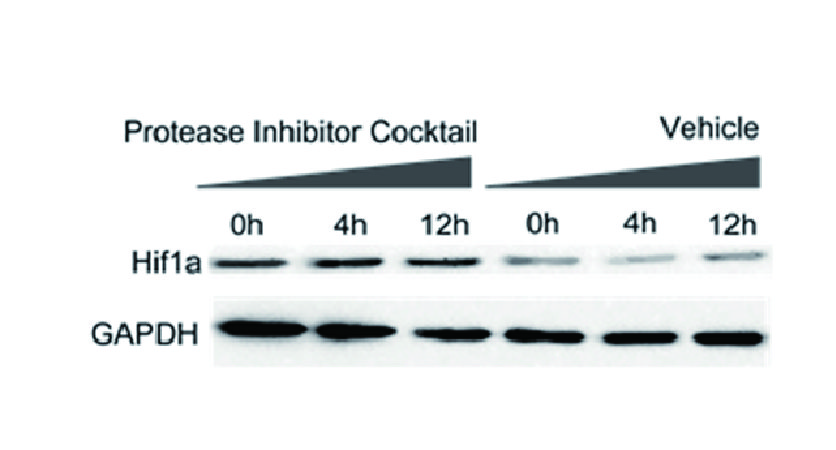
Inhibitor Cocktails
Protect the integrity of proteins from multiple proteases and phosphatases for different applications.
IC50: 0.37 nM for GPCR
Apelin-13 is an endogenous ligand of the APJ receptor.
The apelin receptor APJ, one of a group of G-proteincoupled receptors (GPCR), have recently been paired with their cognate peptide ligands using ‘‘reverse pharmacology’’, and functional evidence suggests a role for this receptor in the regulation of cardiovascular function, fluid homeostasis, and as a coreceptor for HIV infection.
In vitro: Apelin-13 was identified as an endogenous ligand of the APJ receptor, which could activate this G protein-coupled receptor with an EC50 value of 0.37 nM. In addition, the EC50 values for apelin-17 and apelin-36 have been found to be 2.5 and 20 nM, respectively [1].
In vivo: In a previous study, urethane anaesthetised, paralysed and ventilated male SD rats were used to investigate the action of apelin-13 directly microinjected into the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) and the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) on arterial pressure and phrenic nerve activity. Results showed that Apelin-13 microinjections into the NTS led to either apnea or decreased phrenic nerve discharge amplitude by up to 30%. In the RVLM, apelin-13 caused increase in phrenic nerve discharge amplitude depending on the exact site of injection [2].
Clinical trial: Previous clinical study showed that intrabrachial infusions of (Pyr1)apelin-13, acetylcholine, and sodium nitroprusside could cause forearm vasodilatation in patients and control subjects. Systemic infusions of (Pyr1)apelin-13 was able to increase cardiac index and lower mean arterial pressure and peripheral vascular resistance in patients and healthy control subjects but increased heart rate only in control subjects [3].
References:
[1] Lee, D. K.,Cheng, R.,Nguyen, T., et al. Characterization of apelin, the ligand for the APJ receptor. Journal of Neurochemistry 74, 34-41 (2000).
[2] Seyedabadi M, Goodchild AK, Pilowsky PM. Site-specific effects of apelin-13 in the rat medulla oblongata on arterial pressure and respiration. Auton Neurosci. 2002 Oct 31;101(1-2):32-8.
[3] A G Japp, N L Cruden, G Barnes, N van Gemeren, J Mathews, J Adamson, N R Johnston, M A Denvir, I L Megson, A D Flapan, D E Newby. Acute cardiovascular effects of apelin in humans: potential role in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 2010 April 27, 121 (16): 1818-27.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1550.8 |
| Cas No. | 217082-58-1 |
| Formula | C69H111N23O16S |
| Solubility | ≥155.1 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥14.67 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥29.4 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | L-glutaminyl-L-arginyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-leucyl-L-seryl-L-histidyl-L-lysylglycyl-L-prolyl-L-methionyl-L-prolyl-L-phenylalanine |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C([C@H](CCSC)NC(C1N(C(CNC([C@H](CCCCN)NC([C@@H](NC([C@H](CO)NC([C@H](CC(C)C)NC([C@H](CCCNC(N)=N)NC([C@H]2N(C([C@@H](NC([C@@H](N)CCC(N)=O)=O)CCCNC(N)=N)=O)CCC2)=O)=O)=O)=O)CC3=CN=CN3)=O)=O)=O)CCC1)=O)N4[C@H](C(N[C@H](C(O)=O)CC5=CC=CC=C5)=O)CCC4 |
| 运输条件 | 蓝冰运输或根据您的需求运输。 |
| 一般建议 | 不同厂家不同批次产品溶解度各有差异,仅做参考。若实验所需浓度过大至产品溶解极限,请添加助溶剂助溶或自行调整浓度。溶液形式一般不宜长期储存,请尽快用完。 |
| 细胞实验 [1]: | |
|
细胞系 |
血管平滑肌细胞(VSMCs) |
|
溶解方法 |
可溶于DMSO。若获取更高浓度的溶液,可在37℃下孵育10分钟,随后在超声波浴中摇匀。-20℃以下可储存数月。 |
|
反应条件 |
24 h |
|
应用 |
Apelin-13通过诱导磷酸肌醇3激酶(PI3K)/Akt信号转导途径,促进VSMC增殖。Apelin-13(0.5-4 μM)以剂量和时间依赖的方式促进磷酸化PI3K和磷酸化Akt的表达。Apelin-13通过PI3K/Akt信号传导通路促进VSMC增殖。 |
| 动物实验 [2-4]: | |
|
动物模型 |
Wistar大鼠,心肌I/R损伤啮齿动物(小鼠和大鼠)模型 |
|
给药剂量 |
脑室内(ICV)给药,静脉注射(IV)10 nmol |
|
应用 |
在大鼠中,Apelin-13对食物摄入影响不大,但在1小时时,Apelin-13以剂量依赖性方式增加饮酒行为和摄水量。Apelin-13(10 nmol)增加了水分摄入。Apelin-13(10 nmol)在30分钟时显著增加血浆ACTH和皮质酮含量,降低血浆催乳素、LH和FSH含量。在心肌I/R损伤啮齿动物(小鼠和大鼠)模型中,Apelin-13使梗死面积减少43.1%和32.7%。脑室内(ICV)注射1和3 nmol的apelin-13,导致进食和禁食大鼠的食物摄入量降低。 |
|
注意事项 |
由于实验环境的不同,实际溶解度可能与理论值略有不同,请测试室内所有化合物的溶解度。 |
|
References: [1]. Liu C, Su T, Li F, et al. PI3K/Akt signaling transduction pathway is involved in rat vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation induced by apelin-13[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2010, 42(6): 396-402. [2].Taheri S, Murphy K, Cohen M, et al. The effects of centrally administered apelin-13 on food intake, water intake and pituitary hormone release in rats[J]. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 2002, 291(5): 1208-1212. [3].Simpkin J C, Yellon D M, Davidson S M, et al. Apelin-13 and apelin-36 exhibit direct cardioprotective activity against ischemiareperfusion injury[J]. Basic research in cardiology, 2007, 102(6): 518. [4]. Sunter D, Hewson A K, Dickson S L. Intracerebroventricular injection of apelin-13 reduces food intake in the rat[J]. Neuroscience letters, 2003, 353(1): 1-4. |
|
质量控制和MSDS
- 批次:
化学结构