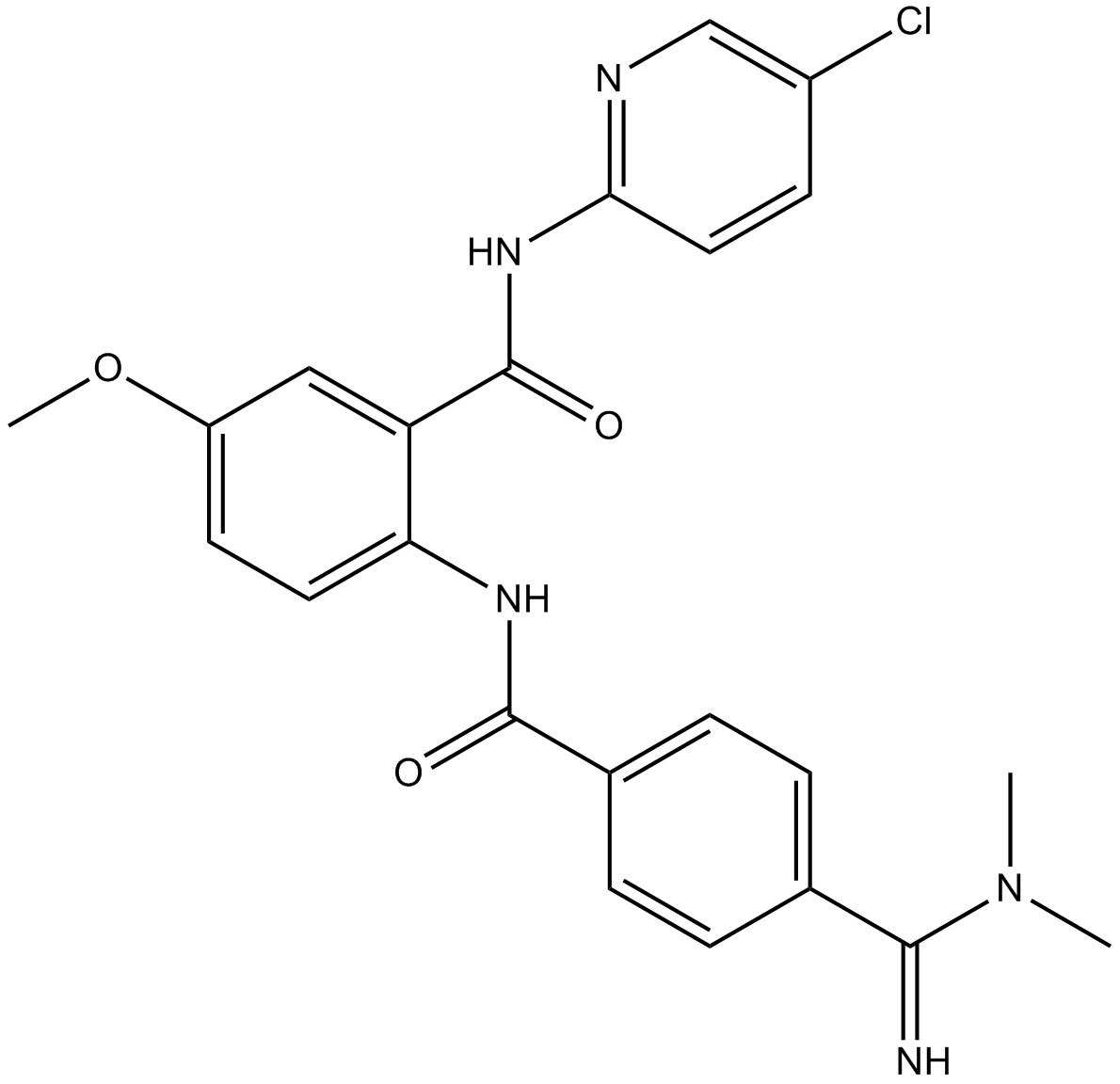
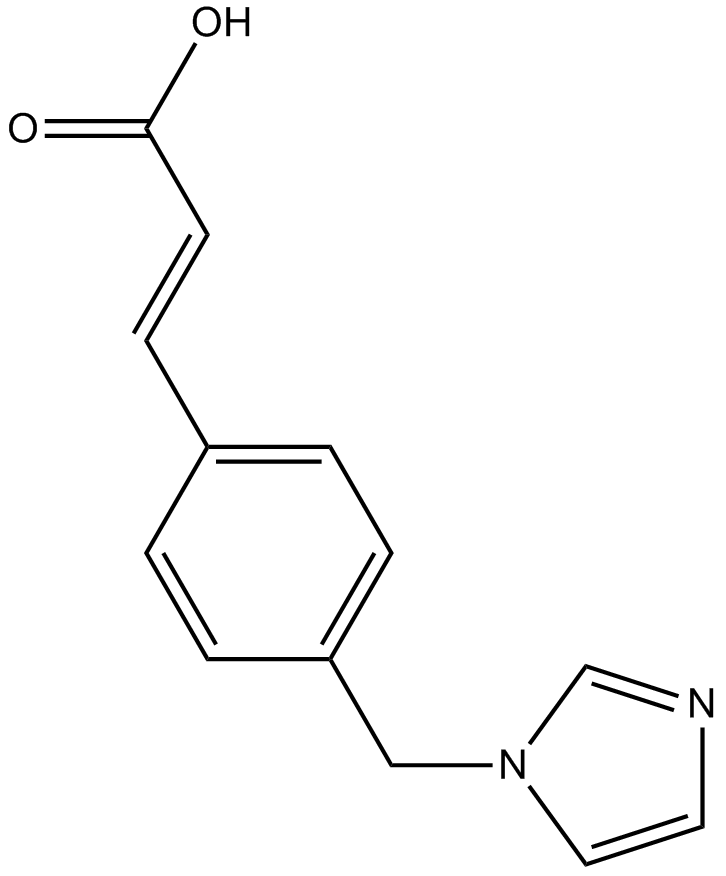
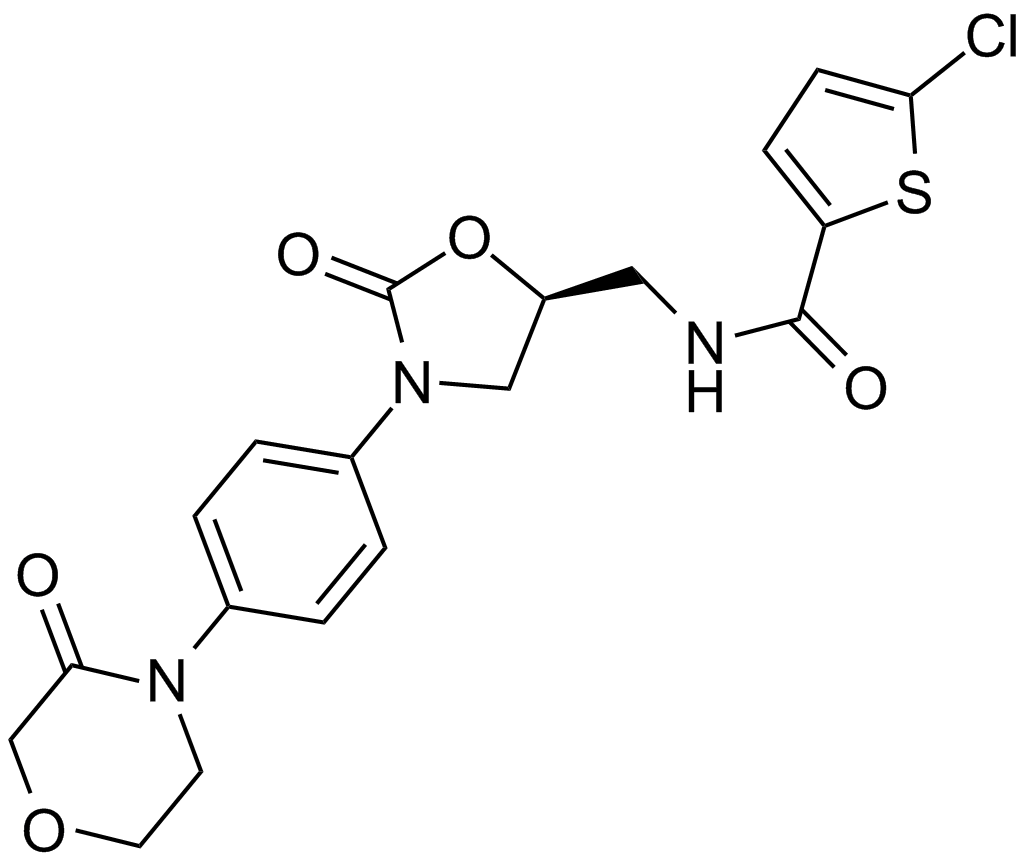
Factor Xa
Factor Xa is a trypsin-like serine protease that catalyzes the cleavage of peptide bonds on the carboxyl side (P’1) of a basic amino acid residue with a preference to cleave peptide bonds of carboxyl function provided by an argininyl residue. Factor Xa plays an essential role in the coagulation cascade catalyzing the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin on surface of vascular cells to link the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways, in which it forms the Ca2+- and phospholipid-dependent prothrombinase complex with cofactor V/Va on activated platelets, monocytes or endothelial cells. Moreover, factor Xa has been found to mediate the stimulation of lymphocyte proliferation, induce the mitogenesis of endothelial and smooth muscle cells, and trigger acute inflammatory responses in vivo.