HIV Protease
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease, belonging to the aspartic proteinase family, is an enzyme encoded by the pol open reading frame (ORF) of HIV genome that catalyze the posttranslational processing of the HIV polyproteins to yield structural proteins of the viral core and enzymes. The chemical structure of a HIV protease molecule is a symmetrical homodimer in which the interface is formed primarily by a four-stranded antiparallel β-sheet. A conserved D25-T26-G27 triad has been identified in each HIV protease monomer, which is positioned in a loop forming part of the catalytic site. HIV protease has been found to cleave peptide bonds in the p55 gag and p160 gag-pol polyproteins as well as in various cellular proteins in vitro, including calmodulin, pro-interleukin 1β and NF-KB.
-
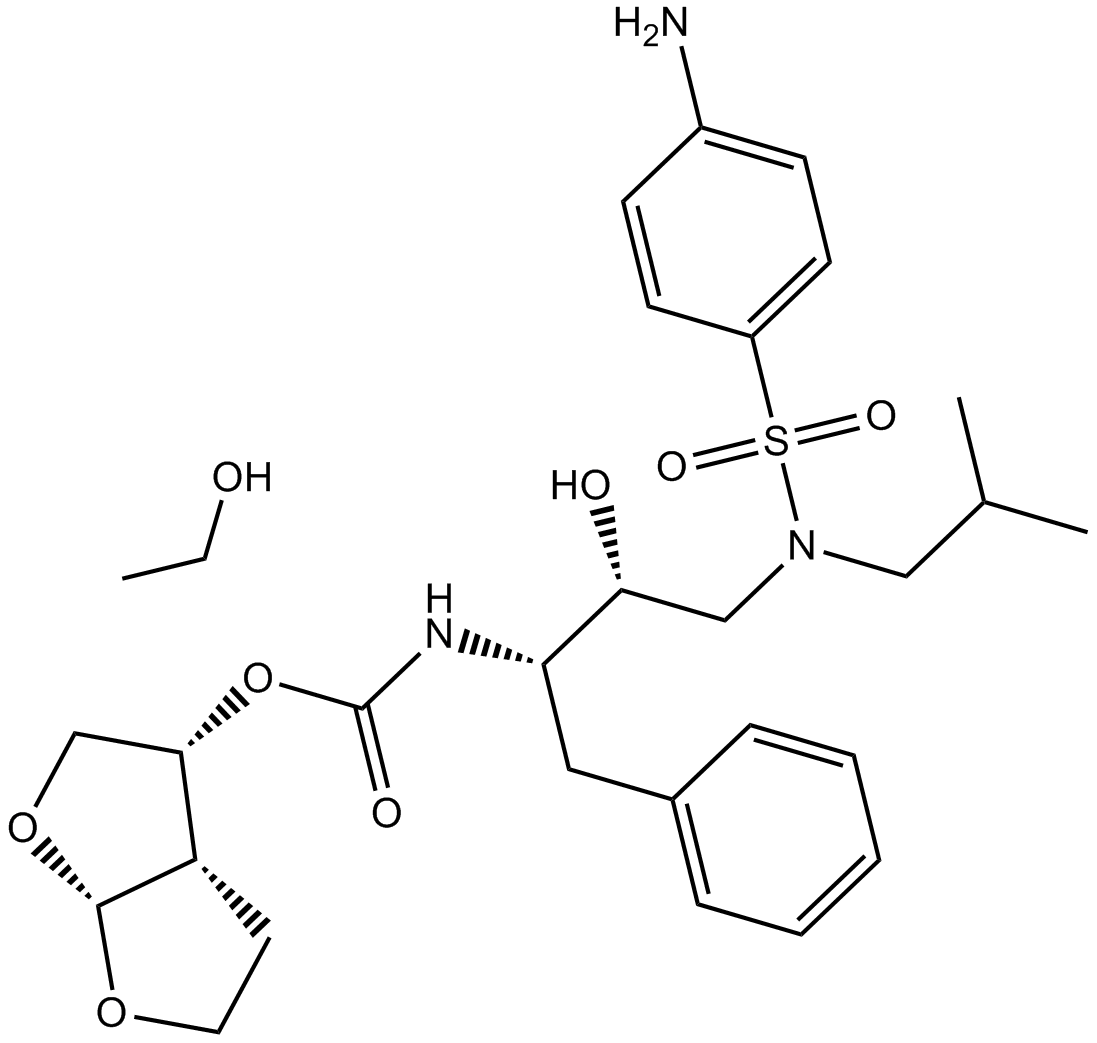 B4950 Darunavir Ethanolate中文名: 地瑞那韦Summary: 非肽HIV蛋白酶抑制剂
B4950 Darunavir Ethanolate中文名: 地瑞那韦Summary: 非肽HIV蛋白酶抑制剂 -
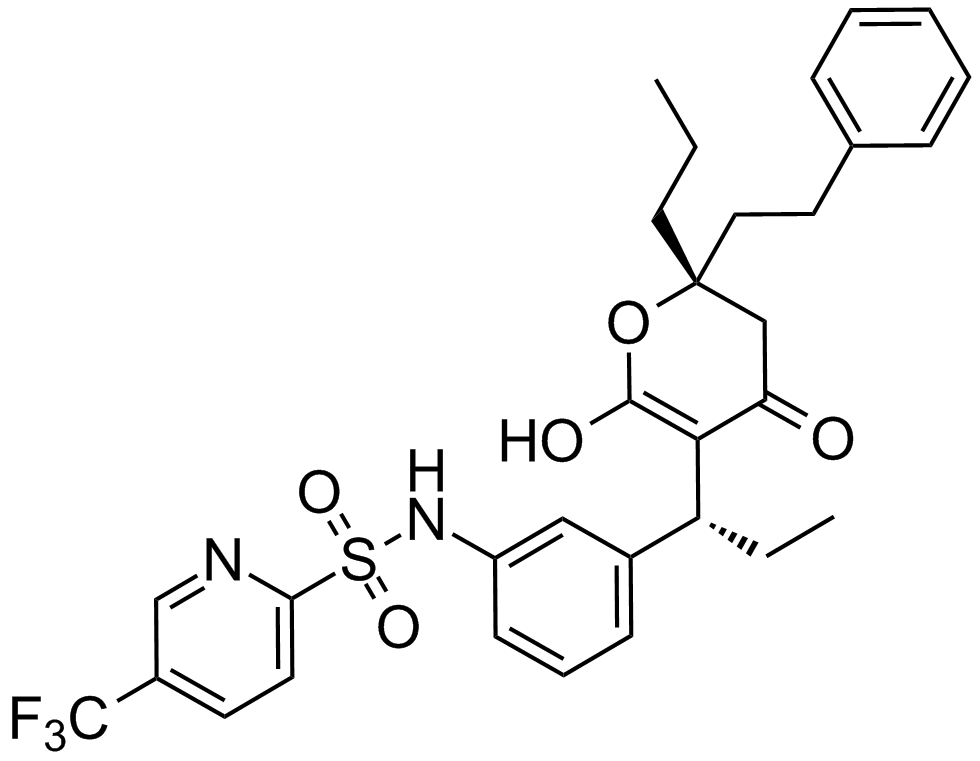 A3876 Tipranavir中文名: 替拉那韦Summary: HIV蛋白酶抑制剂
A3876 Tipranavir中文名: 替拉那韦Summary: HIV蛋白酶抑制剂 -
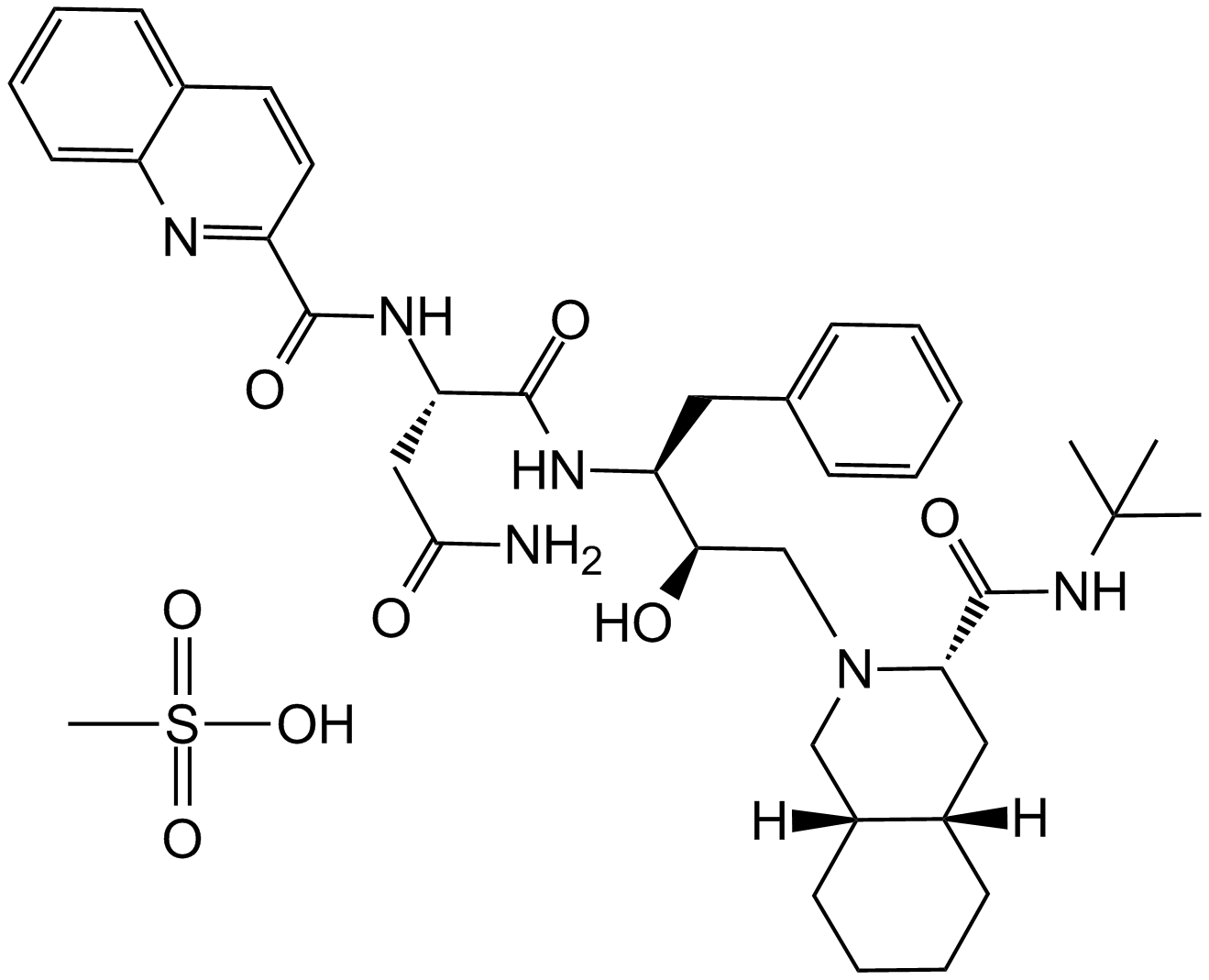 A3791 Saquinavir mesylate中文名: 沙奎那韦甲磺酸盐Summary: HIV蛋白酶抑制剂
A3791 Saquinavir mesylate中文名: 沙奎那韦甲磺酸盐Summary: HIV蛋白酶抑制剂 -
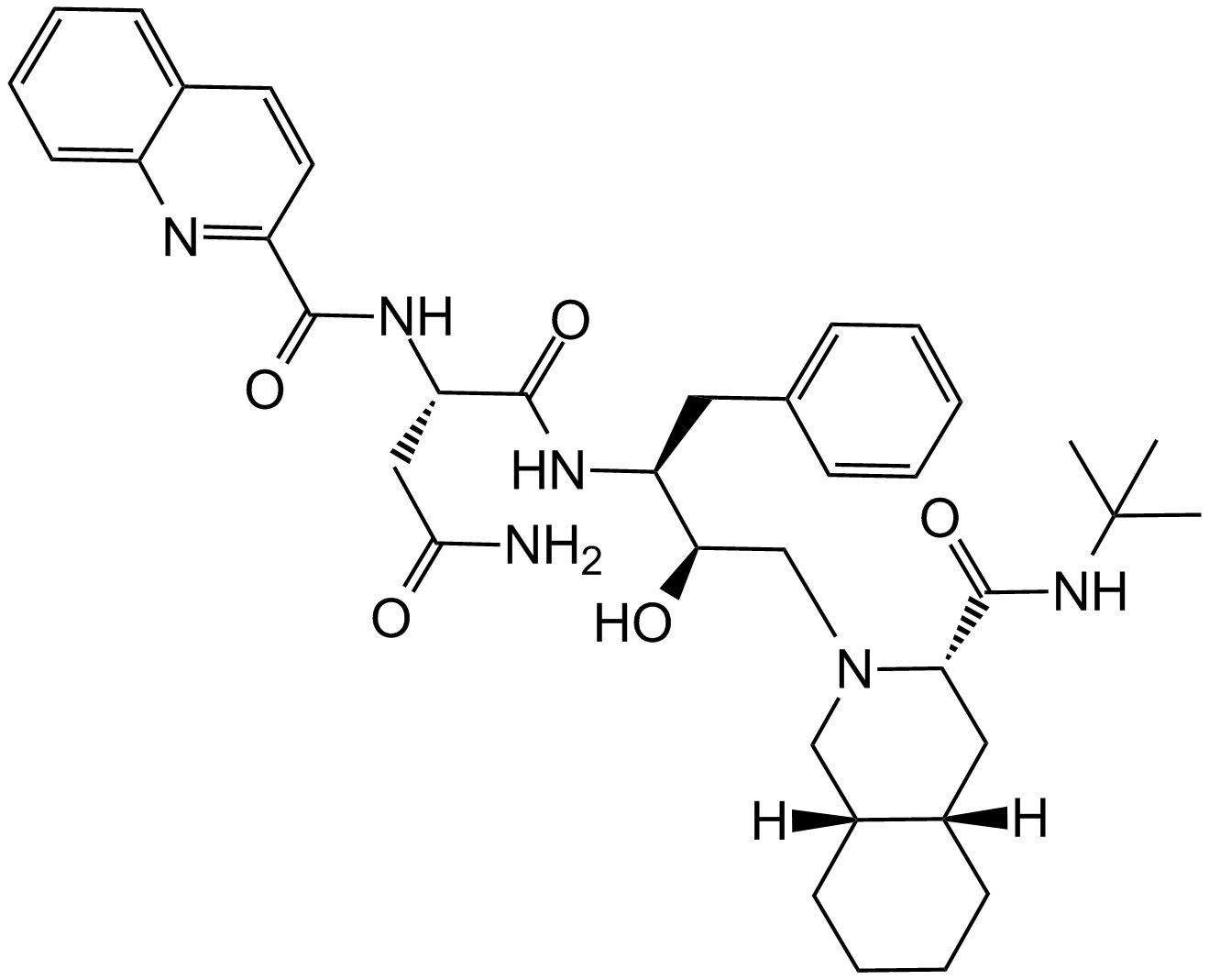 A3790 Saquinavir中文名: 沙奎那韦Summary: HIV蛋白酶抑制剂
A3790 Saquinavir中文名: 沙奎那韦Summary: HIV蛋白酶抑制剂 -
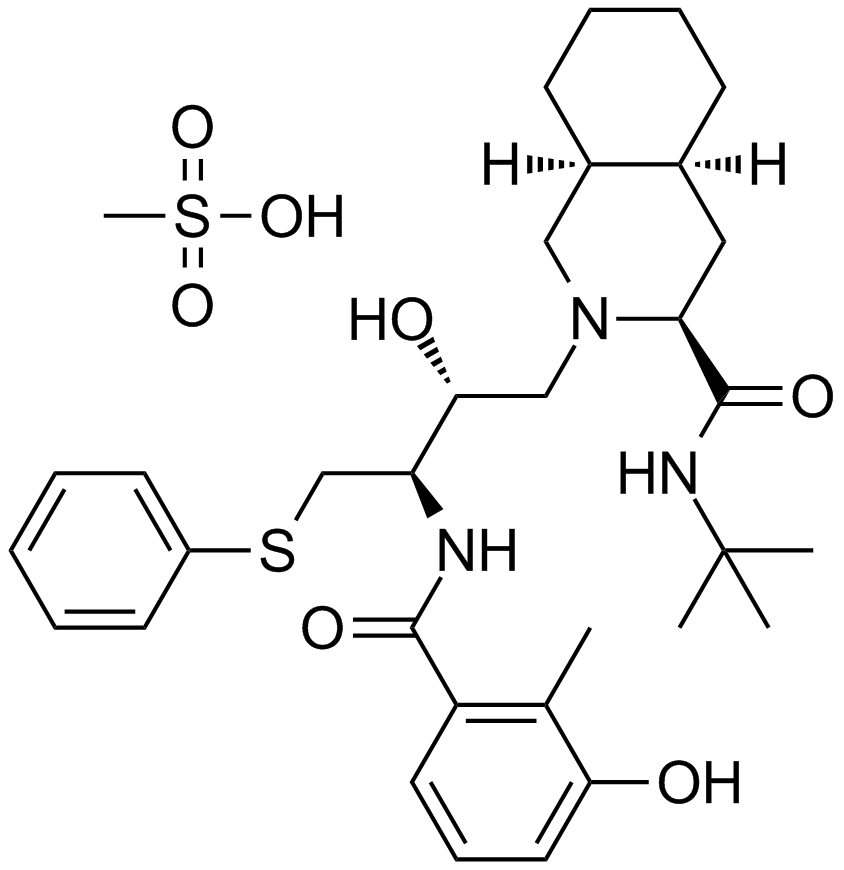 A3653 Nelfinavir Mesylate中文名: 奈非那韦Summary: HIV蛋白酶抑制剂,治疗HIV的抗逆转录病毒药物
A3653 Nelfinavir Mesylate中文名: 奈非那韦Summary: HIV蛋白酶抑制剂,治疗HIV的抗逆转录病毒药物 -
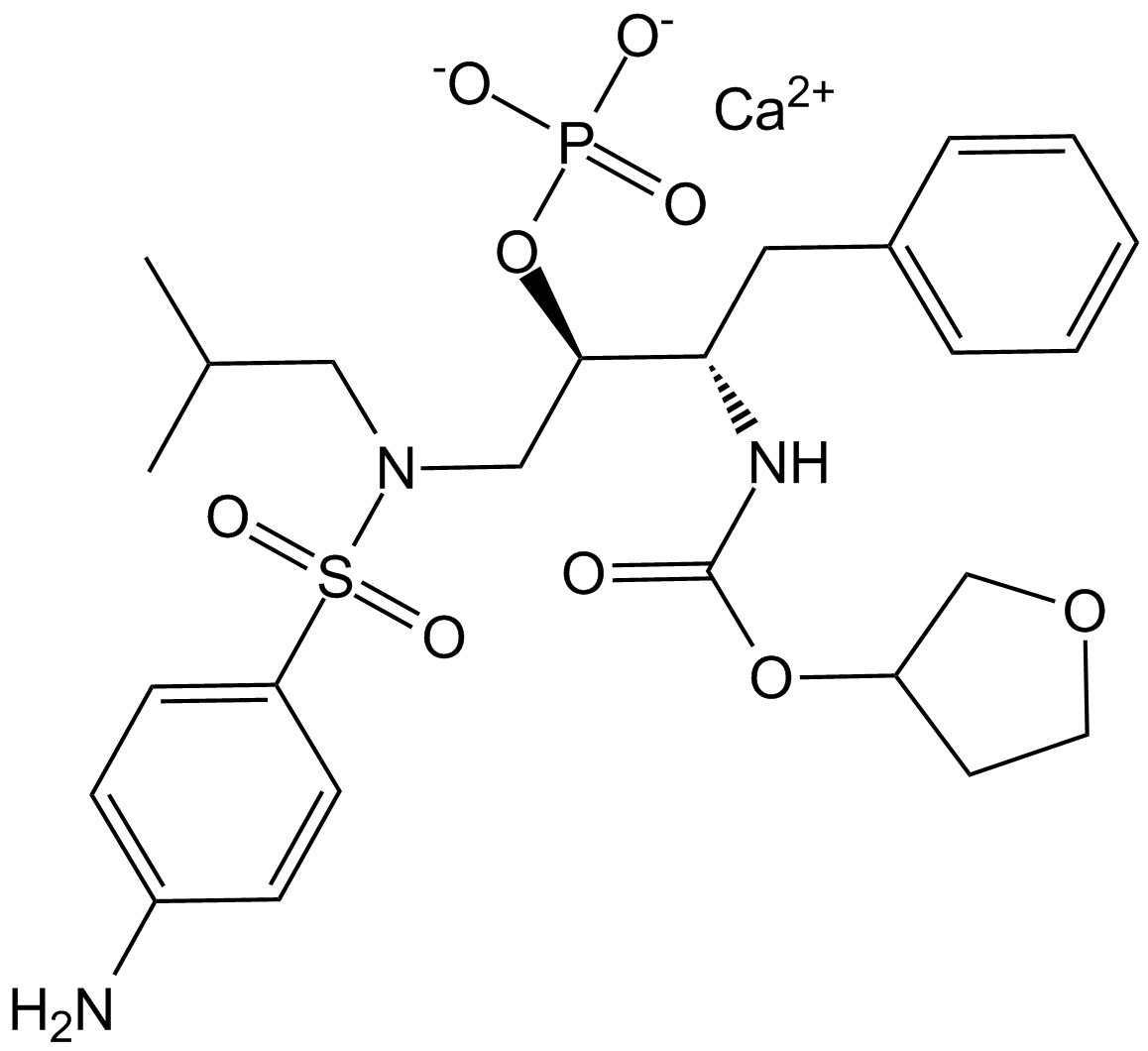 A3421 Fosamprenavir Calcium Salt中文名: 膦沙那韦钙盐Summary: 抗逆转录病毒蛋白酶抑制剂amprenavir的前药。
A3421 Fosamprenavir Calcium Salt中文名: 膦沙那韦钙盐Summary: 抗逆转录病毒蛋白酶抑制剂amprenavir的前药。 -
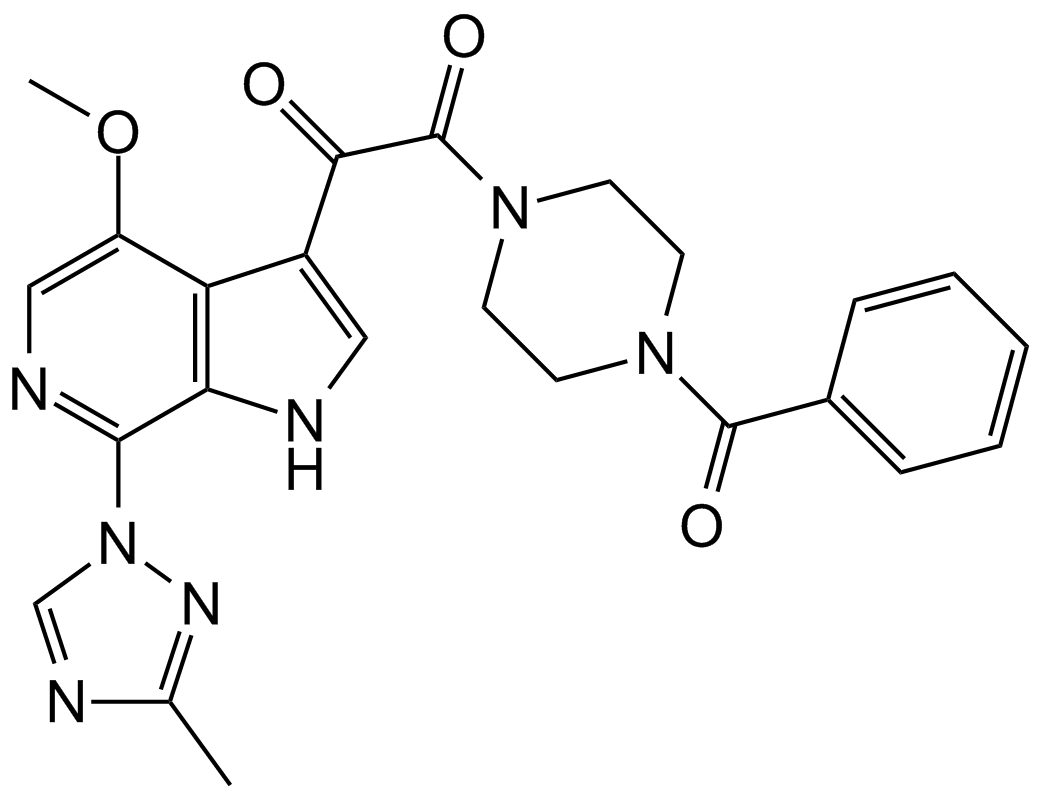 A3253 BMS-6265292 CitationTarget: HIV-1 gp120Summary: HIV-1吸附的抑制剂
A3253 BMS-6265292 CitationTarget: HIV-1 gp120Summary: HIV-1吸附的抑制剂 -
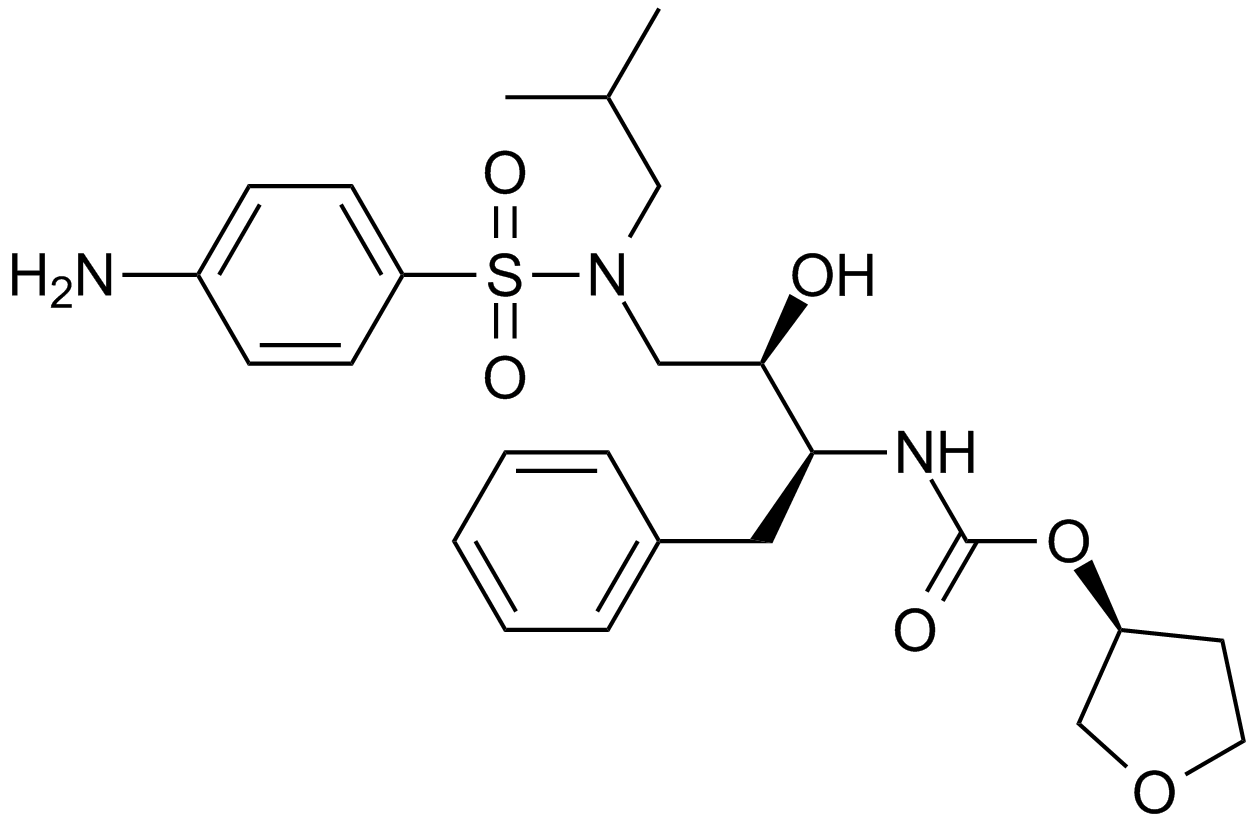 A8201 Amprenavir (agenerase)中文名: 安瑞那韦Summary: HIV-1蛋白酶抑制剂
A8201 Amprenavir (agenerase)中文名: 安瑞那韦Summary: HIV-1蛋白酶抑制剂 -
 A8206 Darunavir2 Citation中文名: 达芦那韦Summary: HIV-1蛋白酶抑制剂
A8206 Darunavir2 Citation中文名: 达芦那韦Summary: HIV-1蛋白酶抑制剂 -
 A8203 Ritonavir中文名: 利托那韦Summary: HIV蛋白酶抑制剂
A8203 Ritonavir中文名: 利托那韦Summary: HIV蛋白酶抑制剂

