Neuroscience

Neurotransmitter receptors function via various G-protein coupled and G-protein independent mechanisms that activate downstream intracellular signaling pathways such as cAMP/PKA, PI3K/AKT, phospholipase A2, and phospholipase C pathways. For instance, dopamine receptors act through adenylate cyclase to activate PKA and other signaling molecules, thereby mediate gene expression through the actions of CREB and other transcription factors. Other neurotransmitters such as NMDAR or AMPAR are associated with ion channels that control flux of Ca2+ and Na+, thus propagating the action potential across the post-synaptic neuron.
Dysfunctions in GABAergic/glutamatergic/serotonergic/dopaminergic pathways result in a broad range of neurological disorders such as chronic pain, neurodegenerative diseases, and insomnia, as well as mental disorders including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depression, and addiction.
-
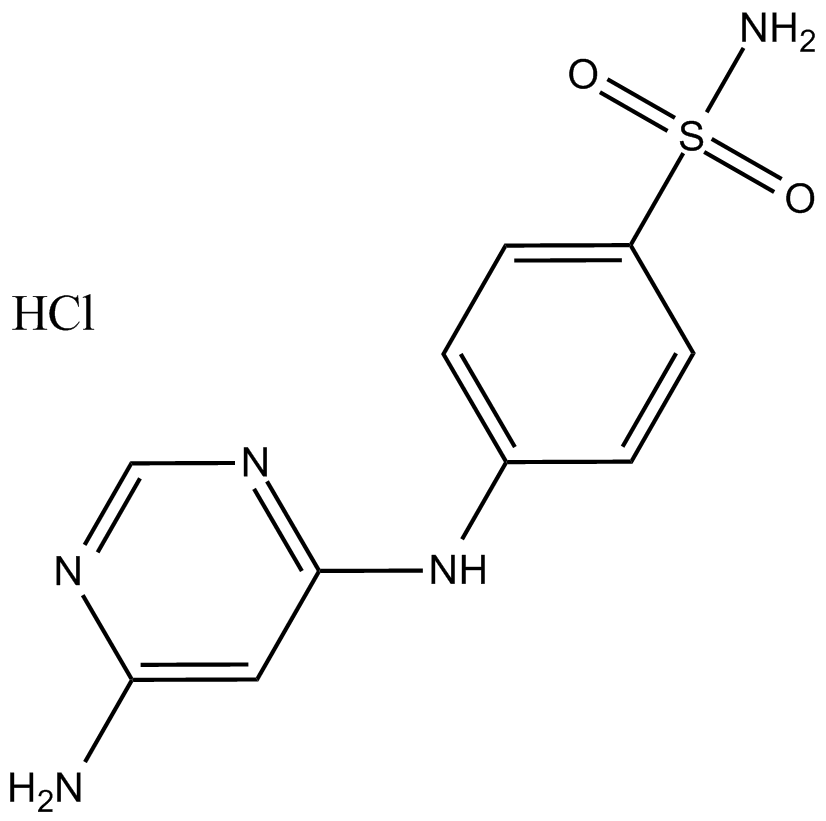 B8543 PNU112455A hydrochlorideSummary: ATP竞争性的CDK2和CDK5抑制剂
B8543 PNU112455A hydrochlorideSummary: ATP竞争性的CDK2和CDK5抑制剂 -
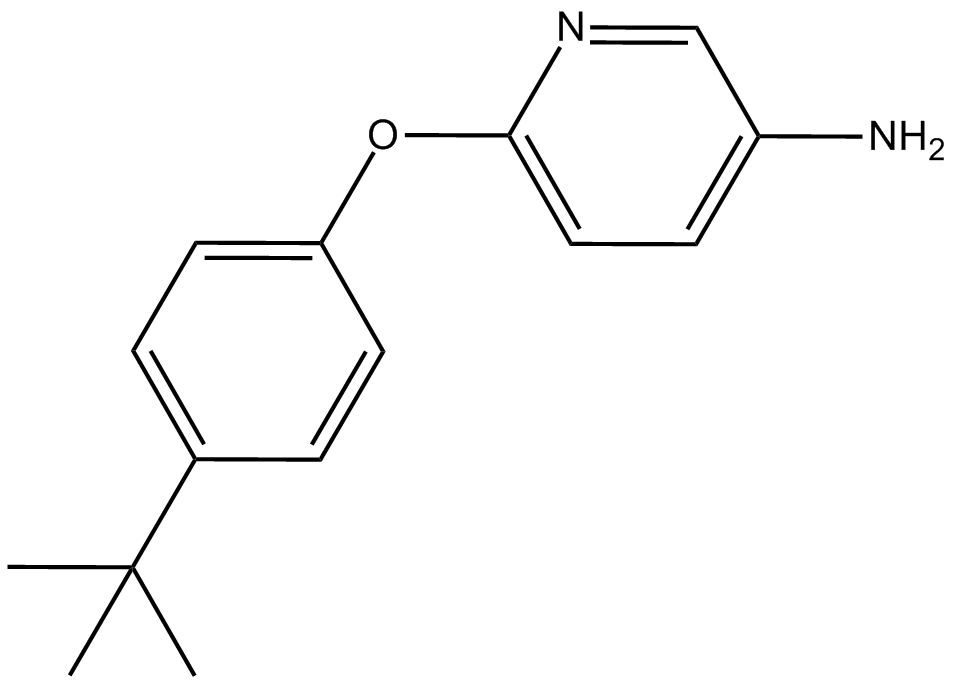 B8529 CB-103Summary: 一种首创的,有口服活性的蛋白相互作用 (PPI) 抑制剂
B8529 CB-103Summary: 一种首创的,有口服活性的蛋白相互作用 (PPI) 抑制剂 -
 B8521 PNU-282987 S enantiomer free baseSummary: α7 烟碱乙酰胆碱受体 (α7 nAChR) 激动剂
B8521 PNU-282987 S enantiomer free baseSummary: α7 烟碱乙酰胆碱受体 (α7 nAChR) 激动剂 -
 B8485 LX2343Summary: 一种 BACE1 酶抑制剂
B8485 LX2343Summary: 一种 BACE1 酶抑制剂 -
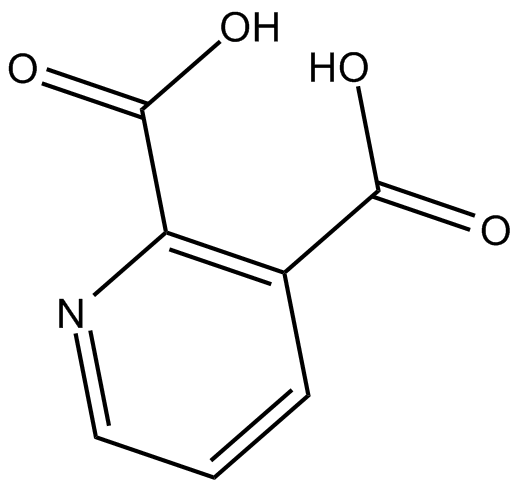 B7858 2-3-Pyridinedicarboxylic acidSummary: NMDA receptor agonist
B7858 2-3-Pyridinedicarboxylic acidSummary: NMDA receptor agonist -
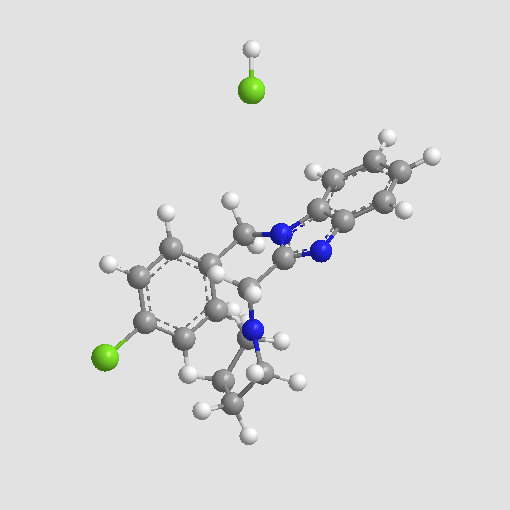 A3316 Clemizole hydrochloride中文名: 盐酸克立咪唑Target: Histamine H1 Receptors|TRPC channelSummary: H1组胺受体拮抗剂
A3316 Clemizole hydrochloride中文名: 盐酸克立咪唑Target: Histamine H1 Receptors|TRPC channelSummary: H1组胺受体拮抗剂 -
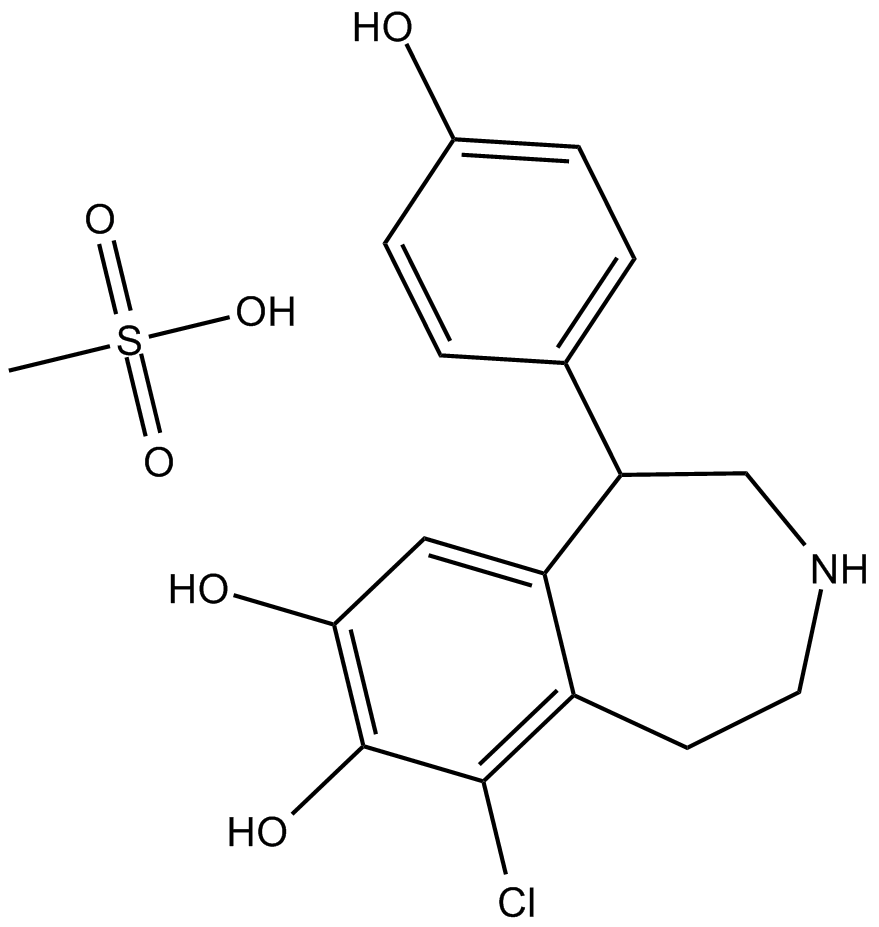 B8681 Fenoldopam (mesylate)中文名: 甲磺酸非诺多泮
B8681 Fenoldopam (mesylate)中文名: 甲磺酸非诺多泮 -
![amyloid A protein fragment [Homo sapiens]](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1053.png) A1053 amyloid A protein fragment [Homo sapiens]Summary: 血浆中与HDL相关的载脂蛋白
A1053 amyloid A protein fragment [Homo sapiens]Summary: 血浆中与HDL相关的载脂蛋白 -
![[Ser25] Protein Kinase C (19-31)](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1033.png) A1033 [Ser25] Protein Kinase C (19-31)Summary: PKC底物
A1033 [Ser25] Protein Kinase C (19-31)Summary: PKC底物 -
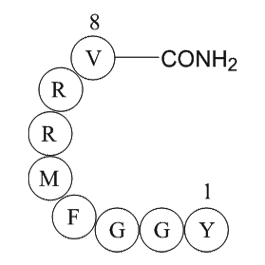 A1032 AdrenorphinSummary: 内源μ/κ阿片受体激动剂
A1032 AdrenorphinSummary: 内源μ/κ阿片受体激动剂

