Gamma Secretase
Gamma secretase (γ-secretase), a member of the intramembrane cleaving protease (i-CLiP) family, is a promiscuous di-aspartyl protease that catalyzes the regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP), in which substrate proteins are cleaved within their membrane-spanning domain. A functional γ-secretase is a multi-protein complex consisting of the catalytic component, presenilin (PSEN), and three protein cofactors, including nicastrin (NCT), anterior-pharynx defective-1 (APH1) and PSEN enhancer-2 (PEN2). So far, 90 substrates of γ-secretase have been identified, which are type-I transmembrane proteins, except for glutamate receptor GluR3, polycystin-1 and glucosaminyltransferase (GnT-V), and appear to function as signaling proteins regulating a wide variety of cellular events, such as Notch signaling pathway.
-
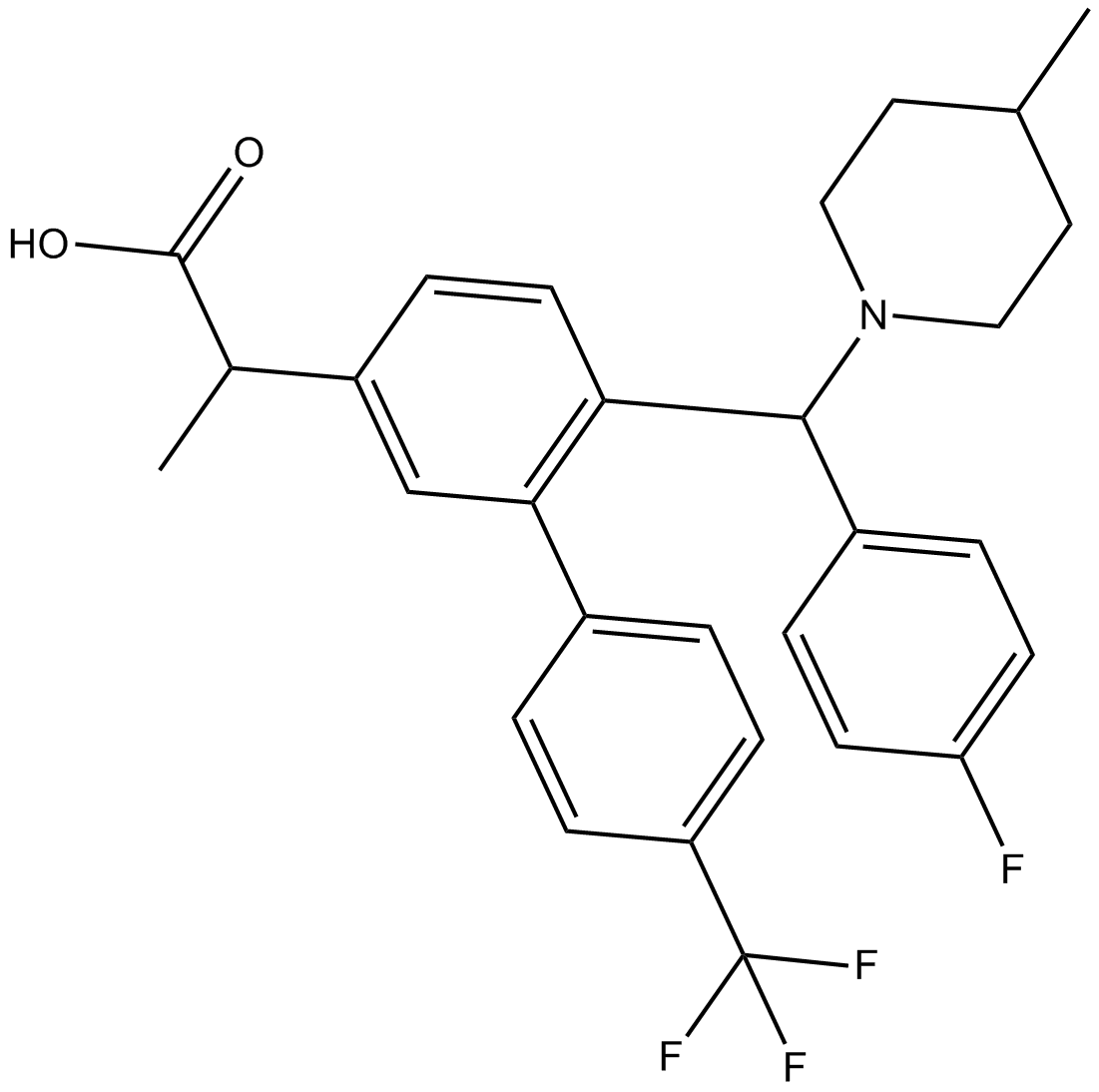 B7719 TC-E 5006Summary: γ分泌酶调节剂
B7719 TC-E 5006Summary: γ分泌酶调节剂 -
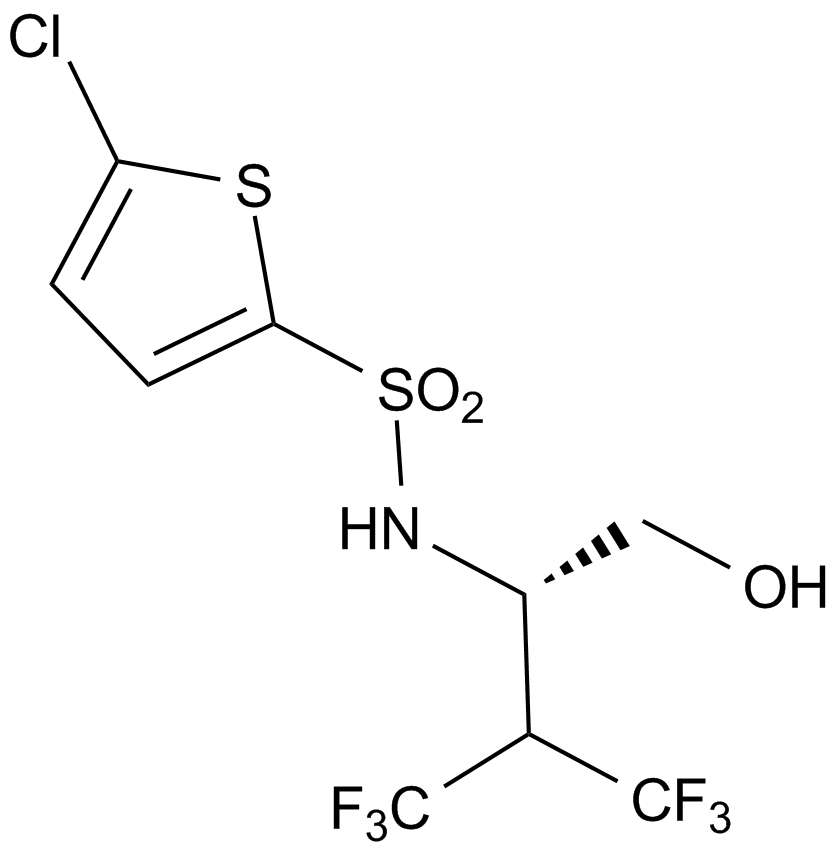 A4406 BegacestatSummary: γ-分泌酶抑制剂
A4406 BegacestatSummary: γ-分泌酶抑制剂 -
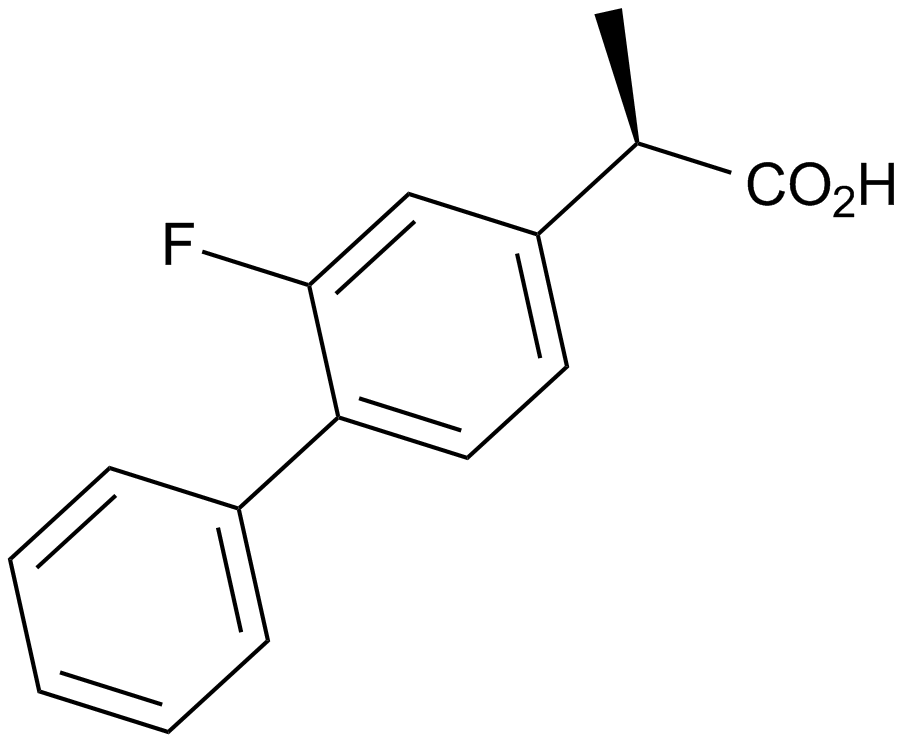 A4402 Flurizan中文名: R-氟比洛芬Summary: 非甾体抗炎药,抑制γ-分泌酶活性
A4402 Flurizan中文名: R-氟比洛芬Summary: 非甾体抗炎药,抑制γ-分泌酶活性 -
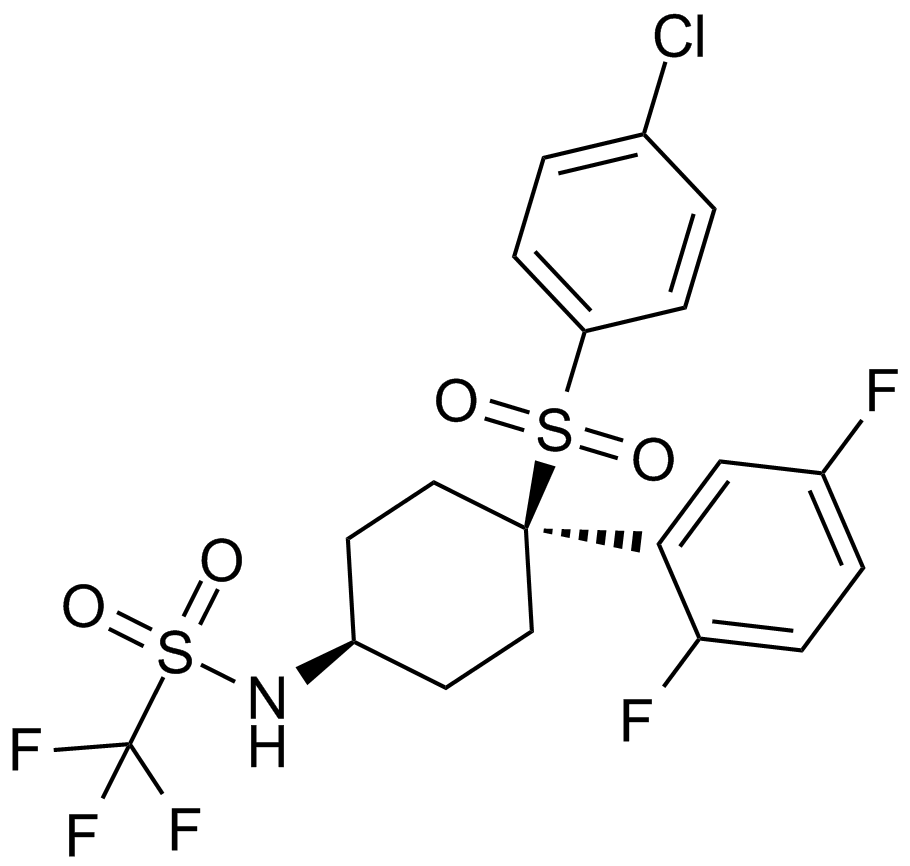 A4405 MRK 560Summary: γ分泌酶抑制剂
A4405 MRK 560Summary: γ分泌酶抑制剂 -
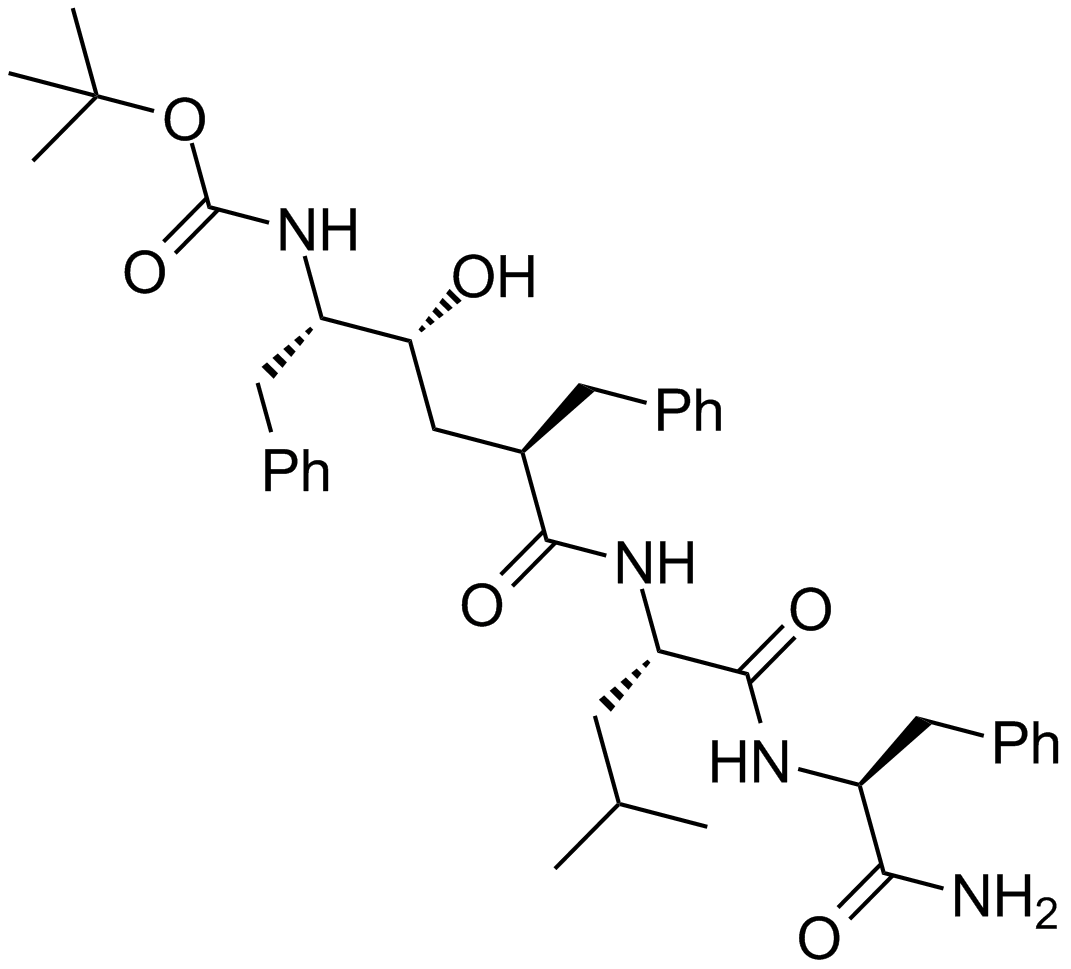 A4404 L-685,458Summary: γ分泌酶抑制剂
A4404 L-685,458Summary: γ分泌酶抑制剂 -
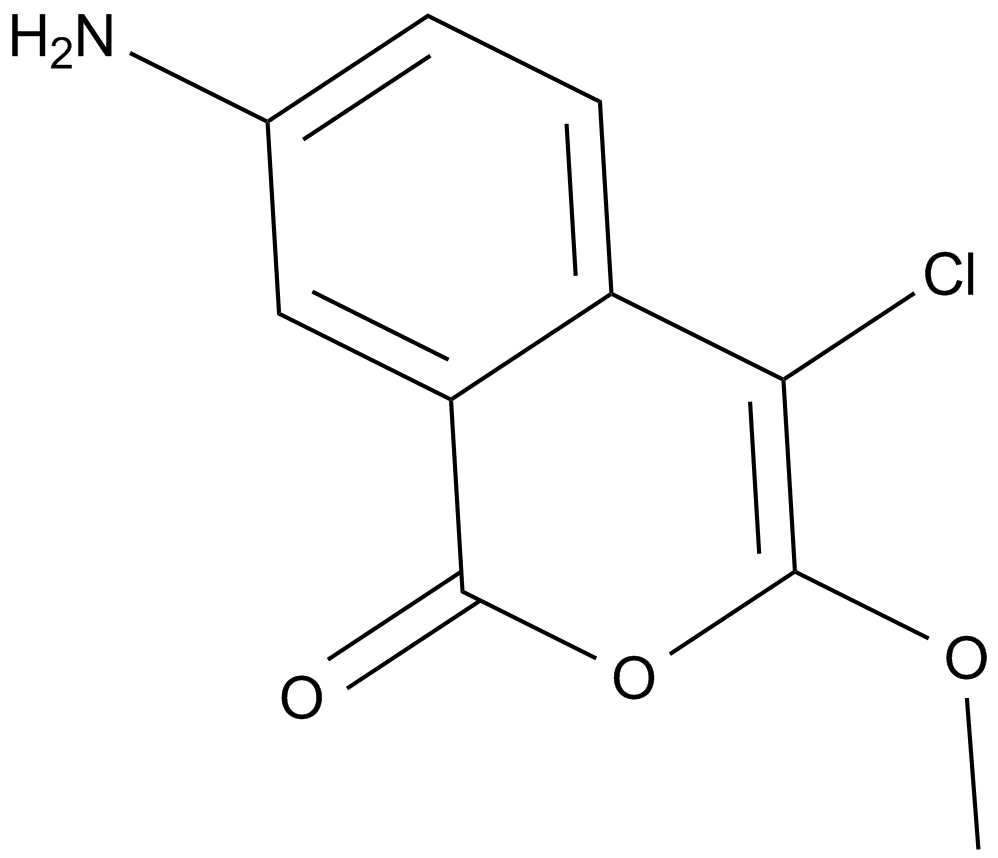 A4403 JLK 6Summary: γ-分泌酶抑制剂
A4403 JLK 6Summary: γ-分泌酶抑制剂 -
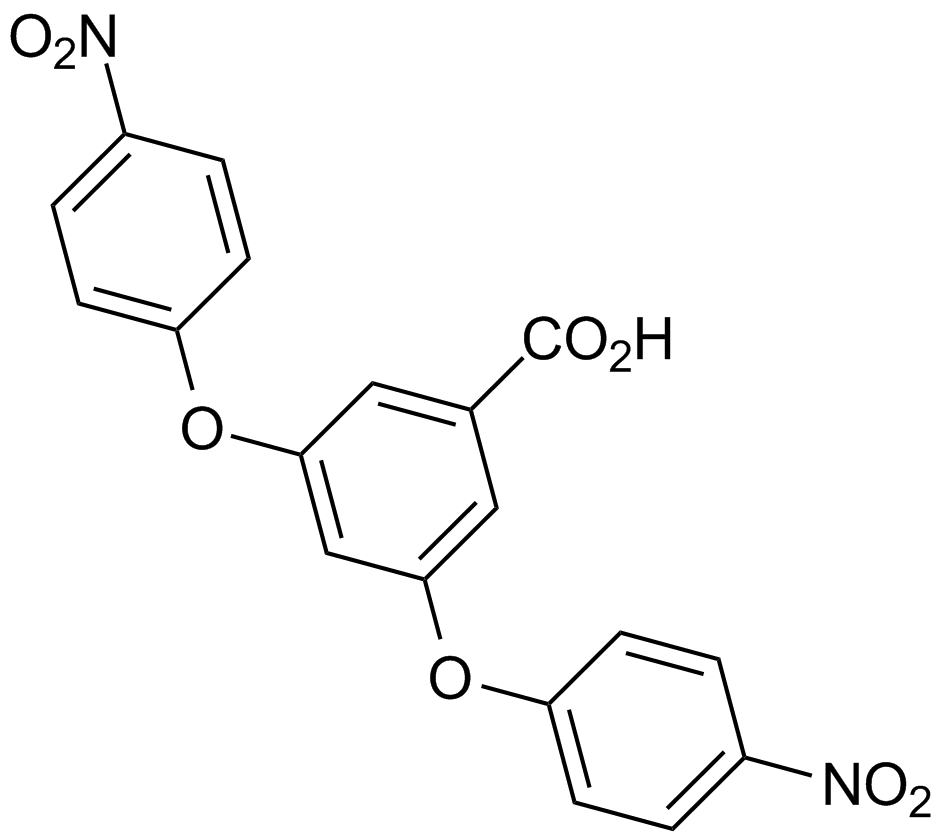 A4401 Compound WSummary: γ-分泌酶抑制剂
A4401 Compound WSummary: γ-分泌酶抑制剂 -
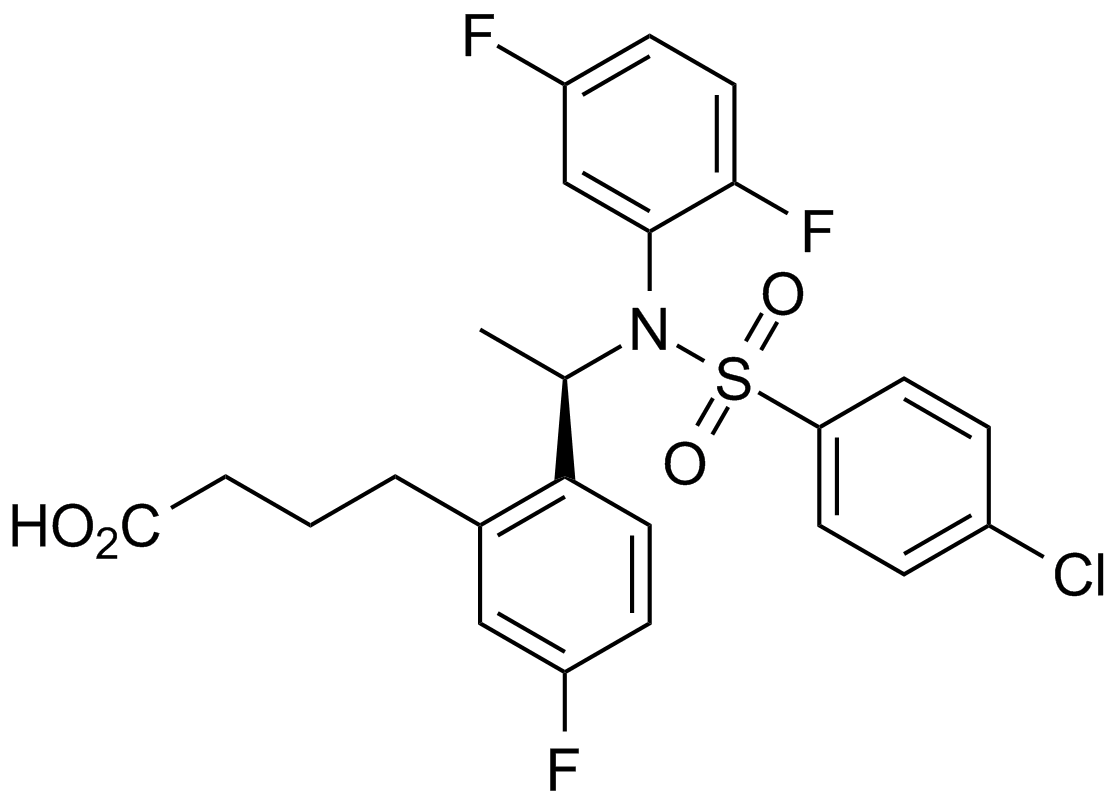 A4400 BMS 299897Summary: γ-分泌酶抑制剂
A4400 BMS 299897Summary: γ-分泌酶抑制剂 -
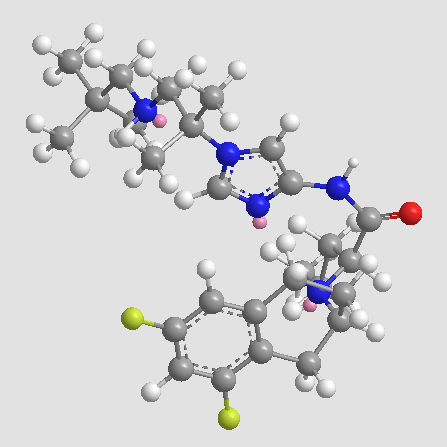 A3711 PF-03084014Summary: γ-分泌酶抑制剂
A3711 PF-03084014Summary: γ-分泌酶抑制剂 -
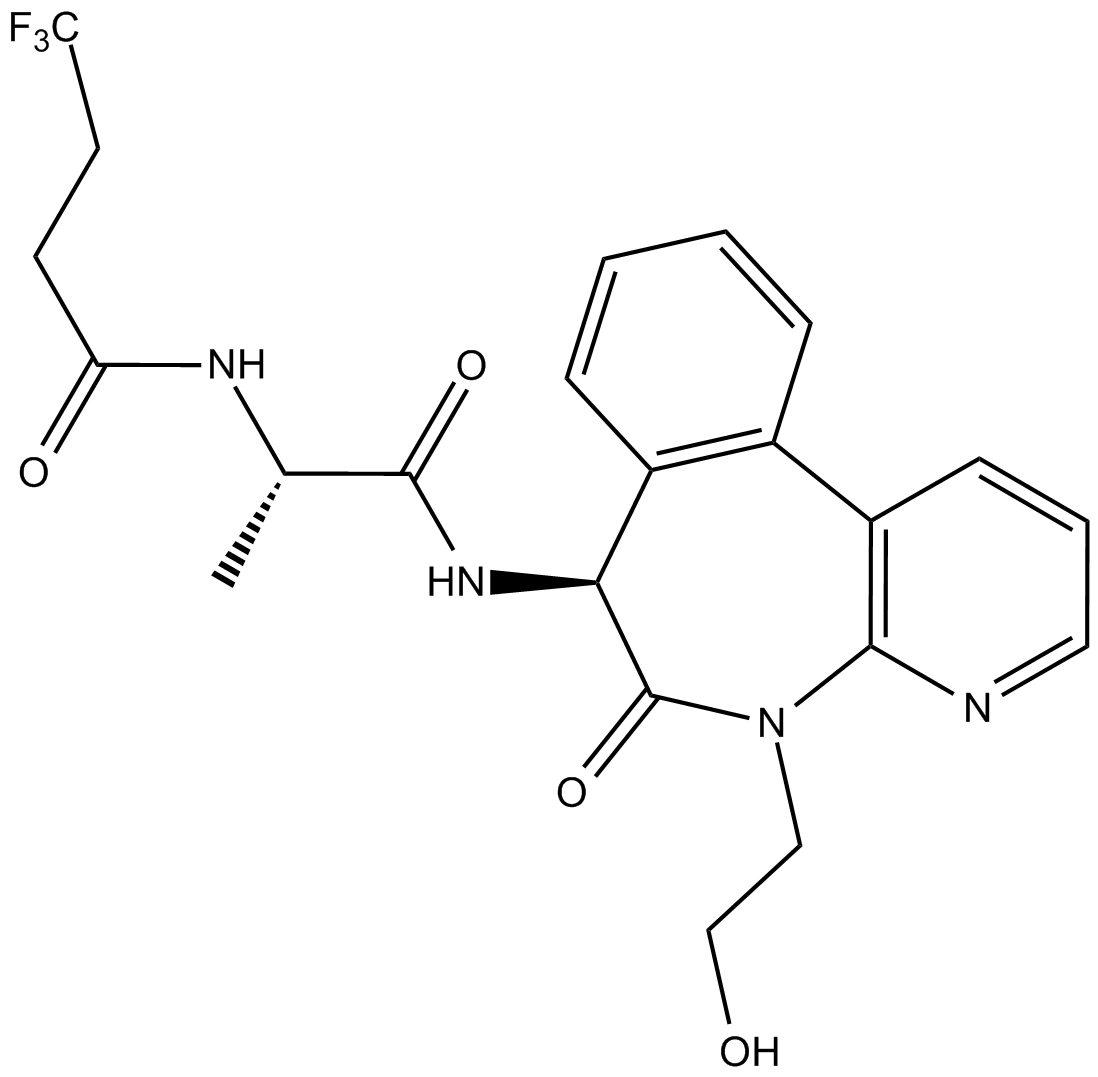 A4023 LY30394781 CitationTarget: NotchSummary: Notch抑制剂
A4023 LY30394781 CitationTarget: NotchSummary: Notch抑制剂

