Aminopeptidase
Aminopeptidases are a group of enzymes widely distributed among bacteria, fungi, animals and plants that catalyze the cleavage of amino acids from the amino terminus of protein or peptide substrates through hydrolysis of peptide bonds near the N-terminal end of a polypeptide chain. Most aminopeptidases are assembled by relatively high mass (50kDa) subunits exhibiting multimeric structures, whereas some are monomeric. The majority of aminopeptidases are zinc metalloenzymes and hence inhibited by the transition-state analog bestatin. Aminopeptidases have been found in many subcellular organelles as well as in cytoplasm and membrane, where they are involved in diverse proteolytic pathways and play an essential role in protein maturation, degradation of non-hormonal and hormonal peptides and possibly determination of protein stability.
-
 C4189 Arphamenine B (hemisulfate)Summary: 氨肽酶B抑制剂
C4189 Arphamenine B (hemisulfate)Summary: 氨肽酶B抑制剂 -
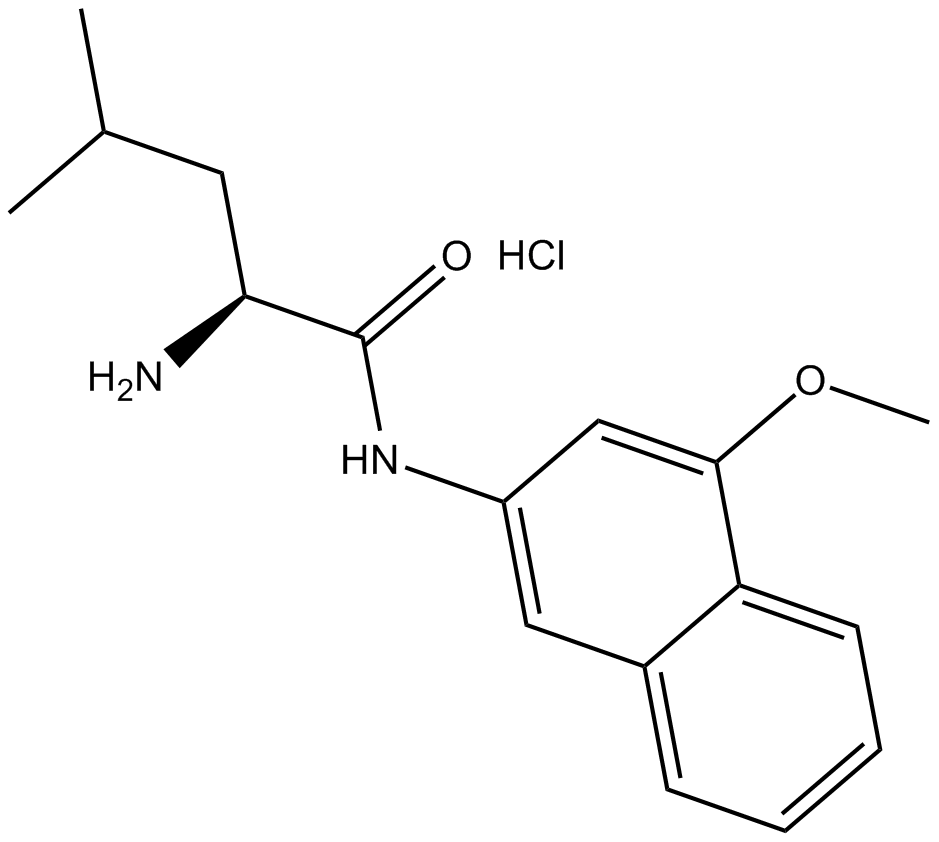 C3708 L-Leucine 4-methoxy-β-naphthylamide (hydrochloride)Summary: 氨基肽酶M和亮氨酸氨基肽酶的底物
C3708 L-Leucine 4-methoxy-β-naphthylamide (hydrochloride)Summary: 氨基肽酶M和亮氨酸氨基肽酶的底物 -
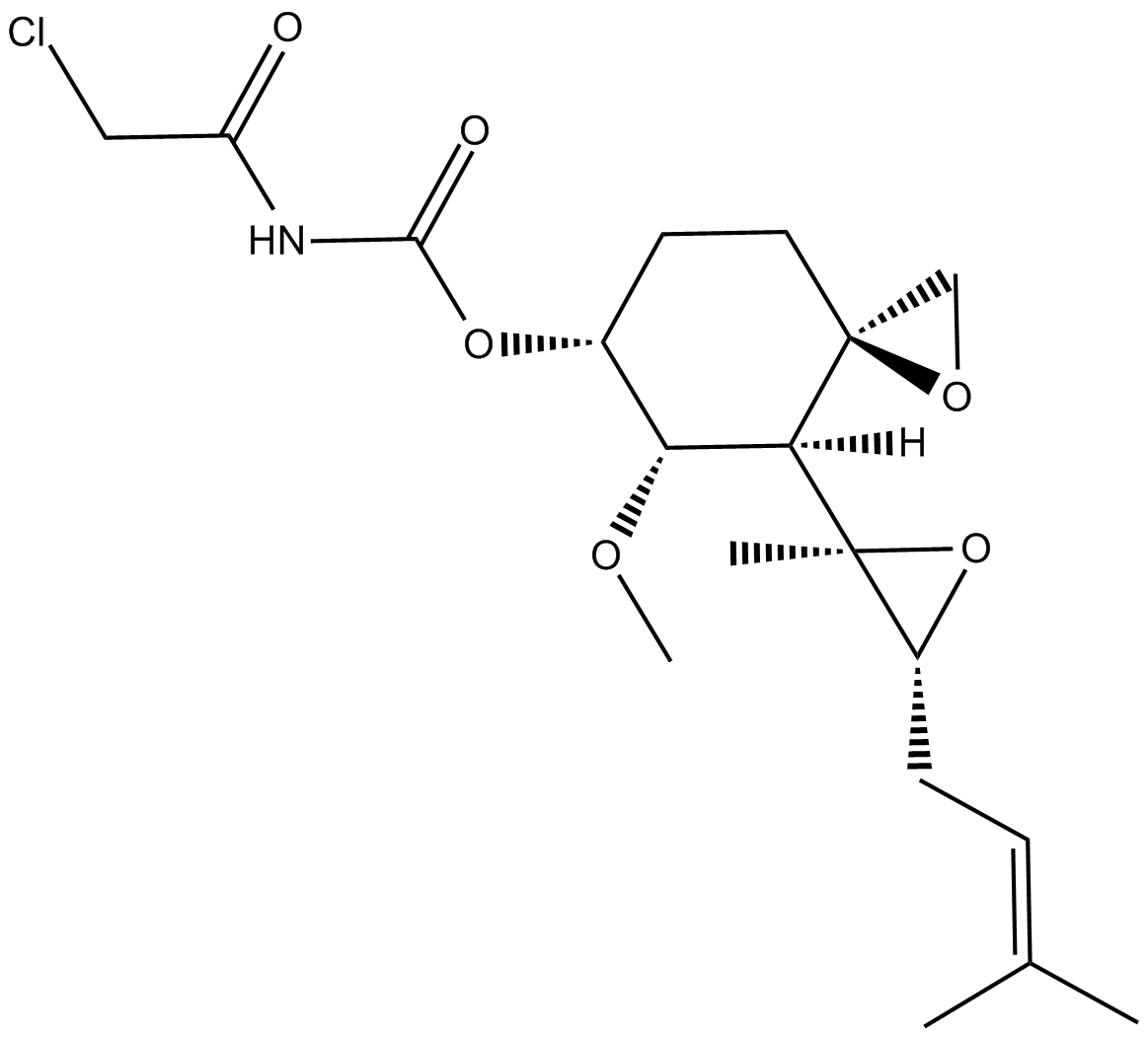 C3622 TNP-470中文名: 夫马菌素醇,夫马吉欣Summary: 甲硫氨酸氨基肽酶-2(MetAP2)抑制剂
C3622 TNP-470中文名: 夫马菌素醇,夫马吉欣Summary: 甲硫氨酸氨基肽酶-2(MetAP2)抑制剂 -
 A8621 Bestatin hydrochloride中文名: 盐酸乌苯美司Target: AminopeptidasesSummary: 氨肽酶N(APN/CD13)和氨肽酶B抑制剂。
A8621 Bestatin hydrochloride中文名: 盐酸乌苯美司Target: AminopeptidasesSummary: 氨肽酶N(APN/CD13)和氨肽酶B抑制剂。 -
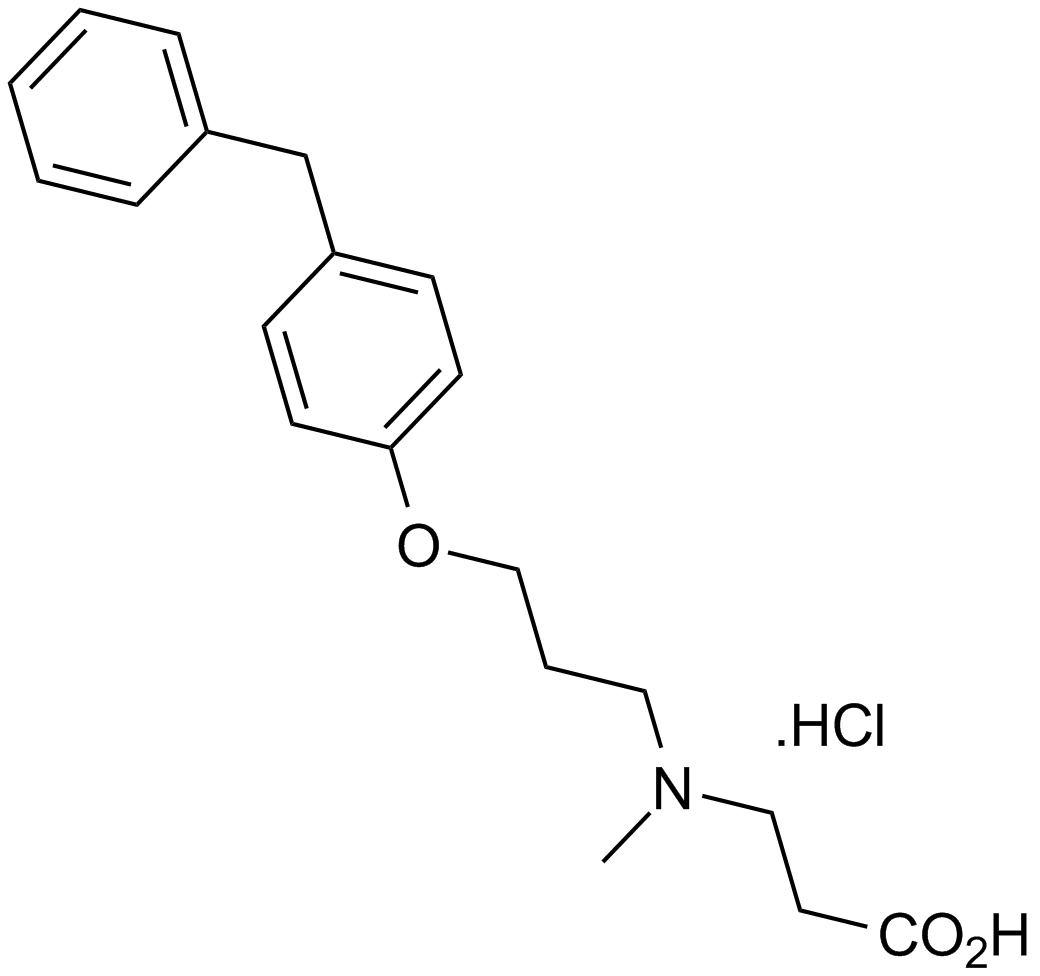 A4408 SC 57461ASummary: LTA4水解酶的强效选择性抑制剂
A4408 SC 57461ASummary: LTA4水解酶的强效选择性抑制剂 -
 A4407 Fumagillin中文名: 烟曲霉素,夫马菌素Summary: 抗生素和抗血管生成剂
A4407 Fumagillin中文名: 烟曲霉素,夫马菌素Summary: 抗生素和抗血管生成剂 -
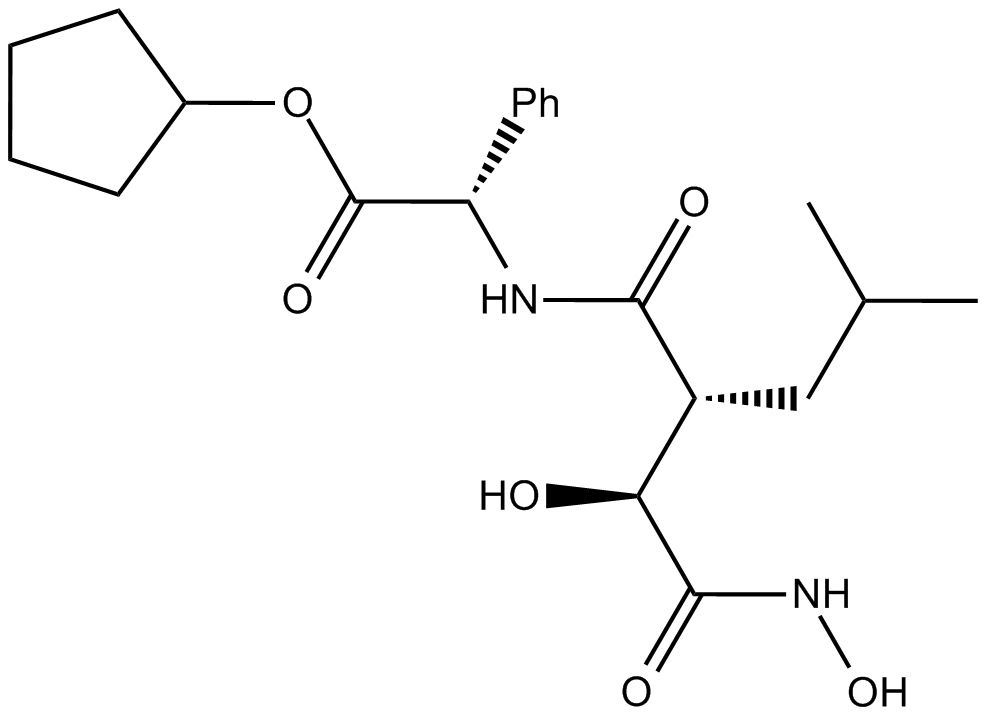 A4355 Tosedostat (CHR2797)1 Citation中文名: 托舍多特Target: AminopeptidasesSummary: 氨肽酶(Aminopeptidase)抑制剂
A4355 Tosedostat (CHR2797)1 Citation中文名: 托舍多特Target: AminopeptidasesSummary: 氨肽酶(Aminopeptidase)抑制剂 -
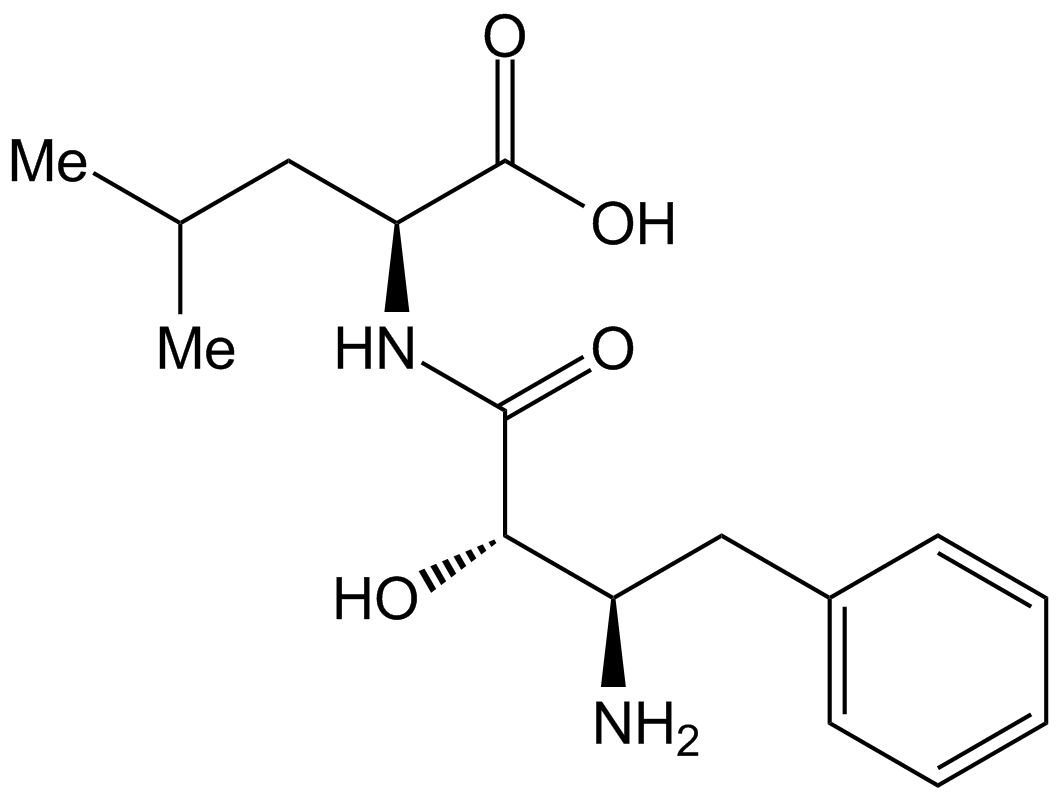 A2575 Bestatin中文名: 乌苯美司Target: AminopeptidasesSummary: 氨肽酶抑制剂
A2575 Bestatin中文名: 乌苯美司Target: AminopeptidasesSummary: 氨肽酶抑制剂

