MAO
Monoamine oxidases (MAOs) are a family of enzymes that oxidize a number of biogenic amines through the production of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Two members of the MAO family have been identified and designated, MAO A and MAO B, which are encoded by two homologous genes comprising 15 exons with identical intro-exon organization and exhibit substrate-specificity. MAO A displays higher affinity towards serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine; while MAO B displays higher affinity towards phenylethylamine and benzylamine. Four highly conserved regions associated with the catalytic activity of mammalian MAO enzymes have been identified, including an ADP binding β-α-β unit, a putative substrate-binding domain, a FAD covalent attachment site, and a C terminus region predicted to form a transmembrane-associated α-helix.
-
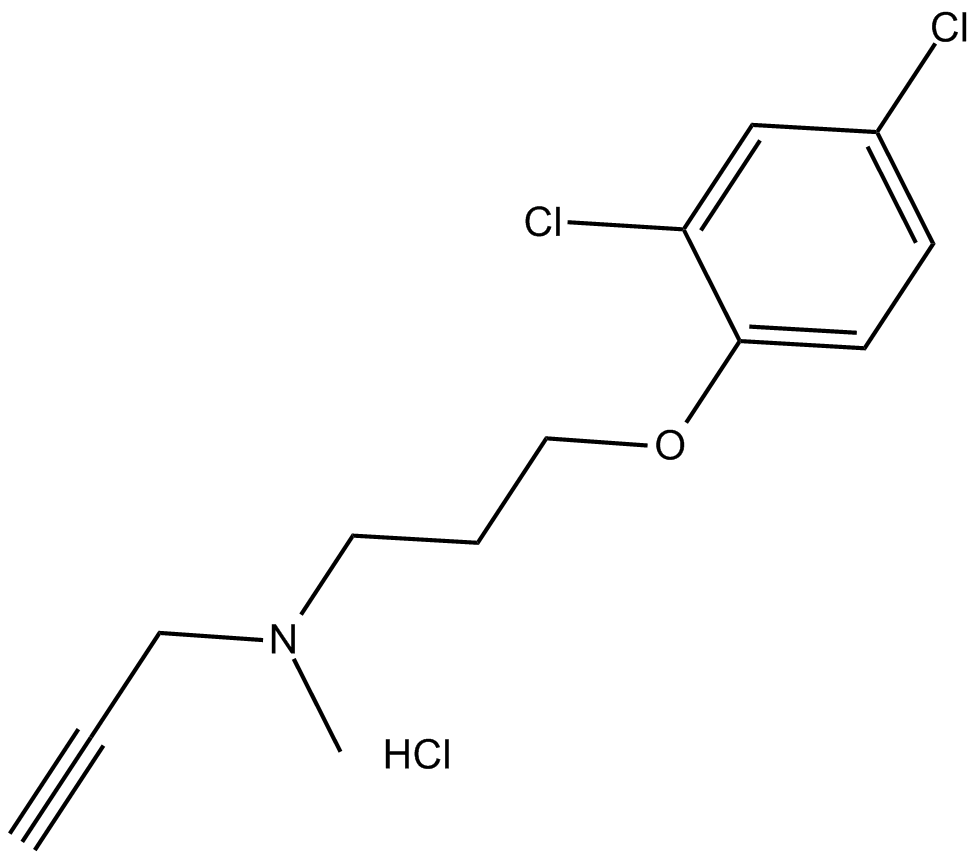 C4137 Clorgyline (hydrochloride)中文名: 盐酸氯吉林Summary: MAO-A抑制剂
C4137 Clorgyline (hydrochloride)中文名: 盐酸氯吉林Summary: MAO-A抑制剂 -
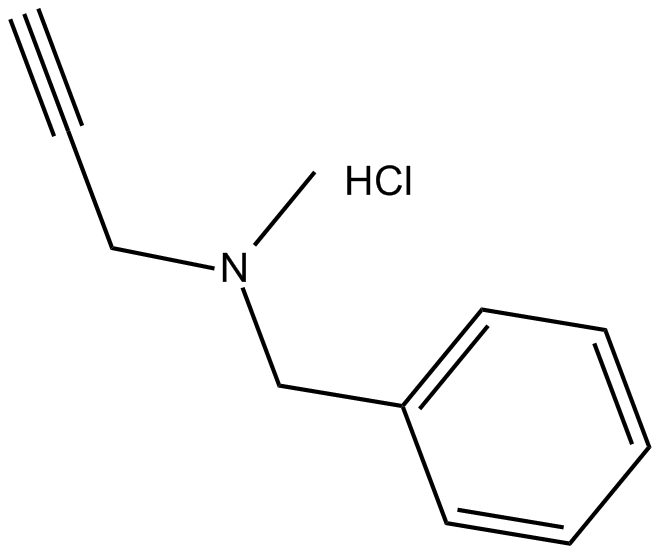 C3106 Pargyline (hydrochloride)中文名: 盐酸帕吉林Summary: MAO抑制剂
C3106 Pargyline (hydrochloride)中文名: 盐酸帕吉林Summary: MAO抑制剂 -
 B6153 Isatin中文名: 靛红Summary: 内源性单胺氧化酶抑制剂
B6153 Isatin中文名: 靛红Summary: 内源性单胺氧化酶抑制剂 -
 A4370 Moclobemide (Ro 111163)中文名: 吗氯贝胺Summary: MAO-A的可逆抑制剂
A4370 Moclobemide (Ro 111163)中文名: 吗氯贝胺Summary: MAO-A的可逆抑制剂 -
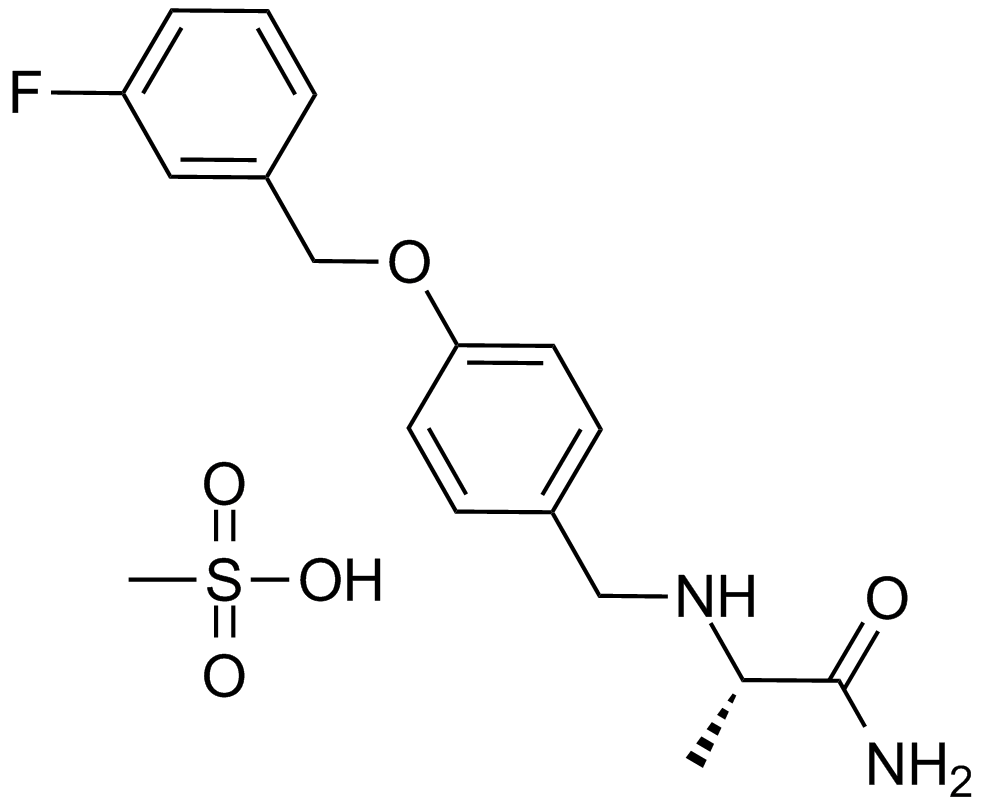 A4368 Safinamide Mesylate中文名: 沙芬酰胺甲磺酸盐Summary: MAO-B抑制剂
A4368 Safinamide Mesylate中文名: 沙芬酰胺甲磺酸盐Summary: MAO-B抑制剂 -
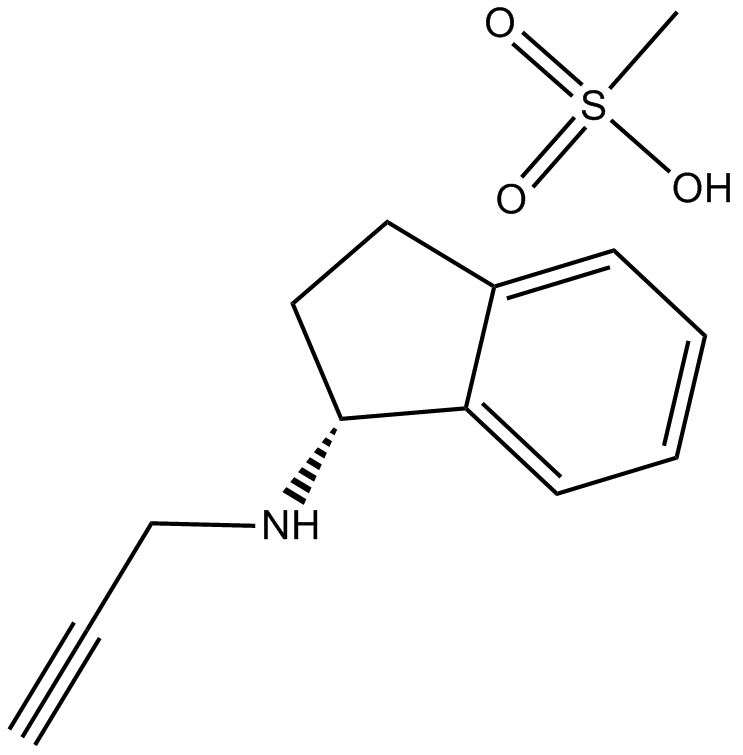 A4366 Rasagiline Mesylate中文名: 甲磺酸雷沙吉兰Summary: MAO-B抑制剂
A4366 Rasagiline Mesylate中文名: 甲磺酸雷沙吉兰Summary: MAO-B抑制剂

