JAK
Janus kinases (JAKs), belonging to a distinct family of tyrosine kinases, are non-receptor tyrosine kinases that transduce signals of cytokine receptors via diverse signal transduction pathways. Mammalian JAK family consists of four structurally similar members, JAK1, JAK2, JAK3 and Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2), which are characterized by containing seven JAK homology (JH) domains. The presence of JH1 and JH2 domains is the most intriguing feature of JAK proteins. JH1 domain is the main catalytic domain; while JH2 is usually considered as a catalytically inactive pseudokinase domain. However, results of recent studies have shown that JH2 acts as a dual-specificity protein kinase to phosphorylate two regulatory sites (Ser523 and Tyr570) in JAK2.
-
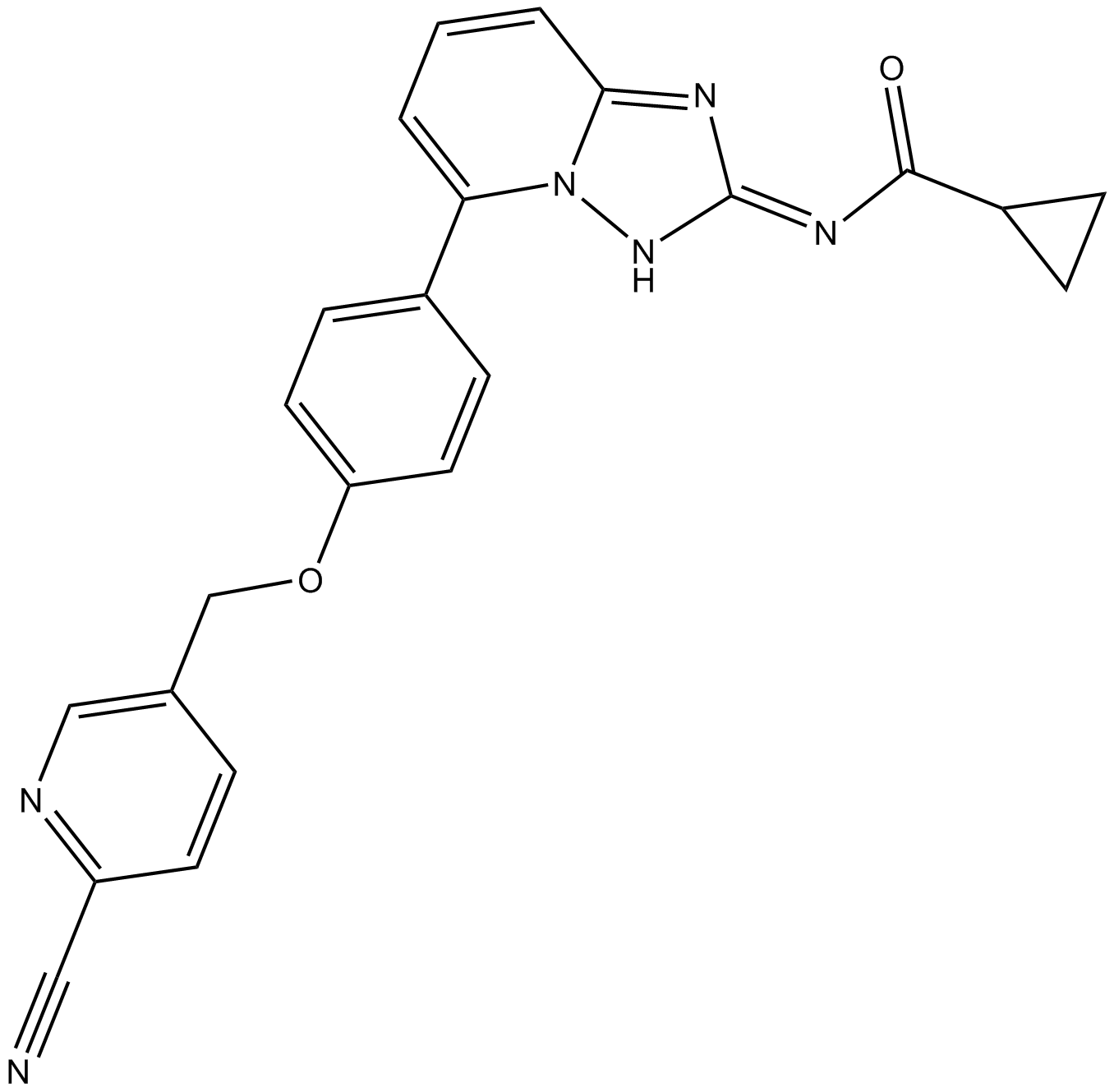 B6116 GLPG0634 analogueSummary: JAK1抑制剂
B6116 GLPG0634 analogueSummary: JAK1抑制剂 -
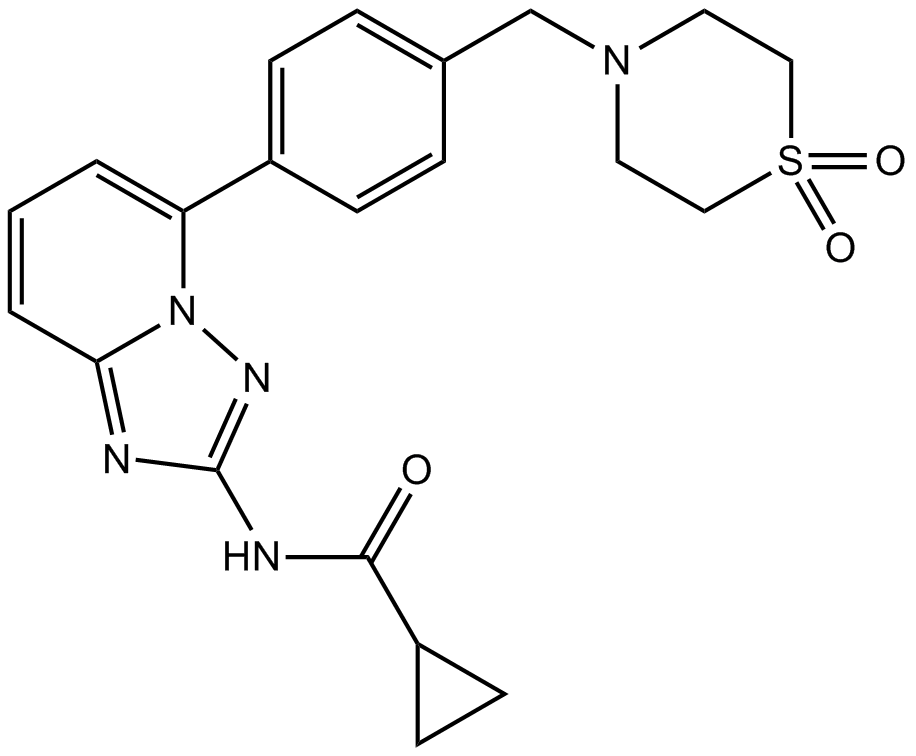 B1130 GLPG06341 Citation中文名: 菲戈替尼Target: JAKSummary: JAK1抑制剂
B1130 GLPG06341 Citation中文名: 菲戈替尼Target: JAKSummary: JAK1抑制剂 -
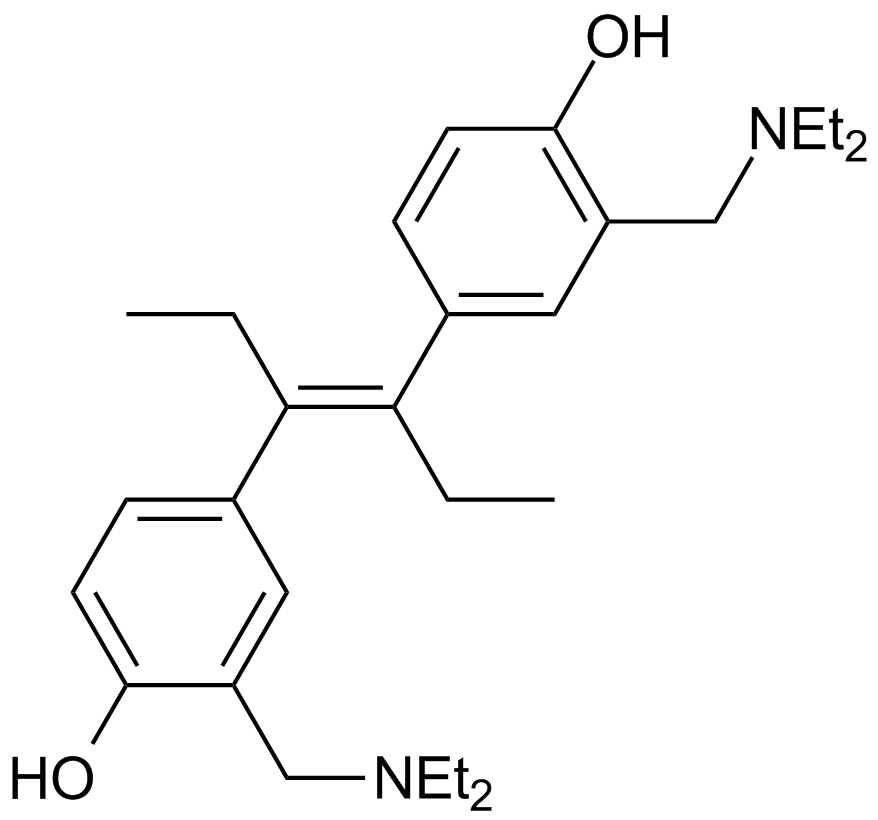 A4514 NSC 33994Summary: 选择性JAK2抑制剂
A4514 NSC 33994Summary: 选择性JAK2抑制剂 -
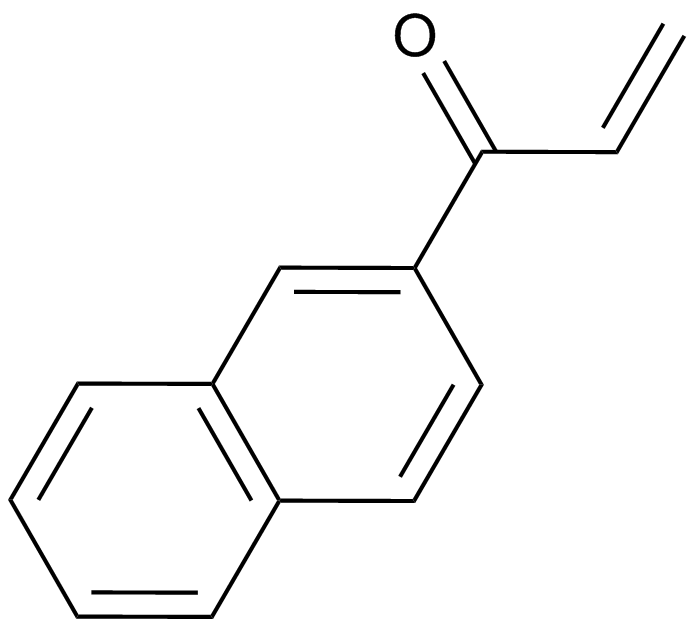 A4517 ZM 449829Summary: JAK3抑制剂
A4517 ZM 449829Summary: JAK3抑制剂 -
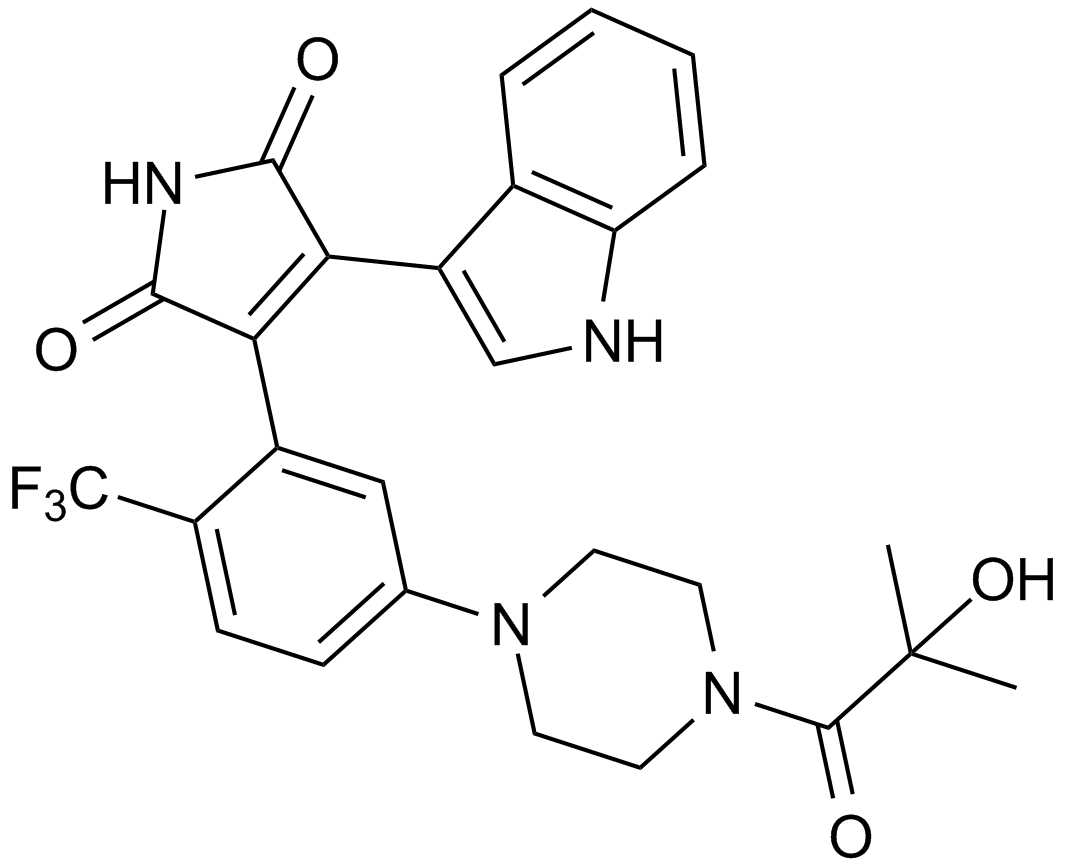 A4516 TCS 21311Summary: JAK3抑制剂
A4516 TCS 21311Summary: JAK3抑制剂 -
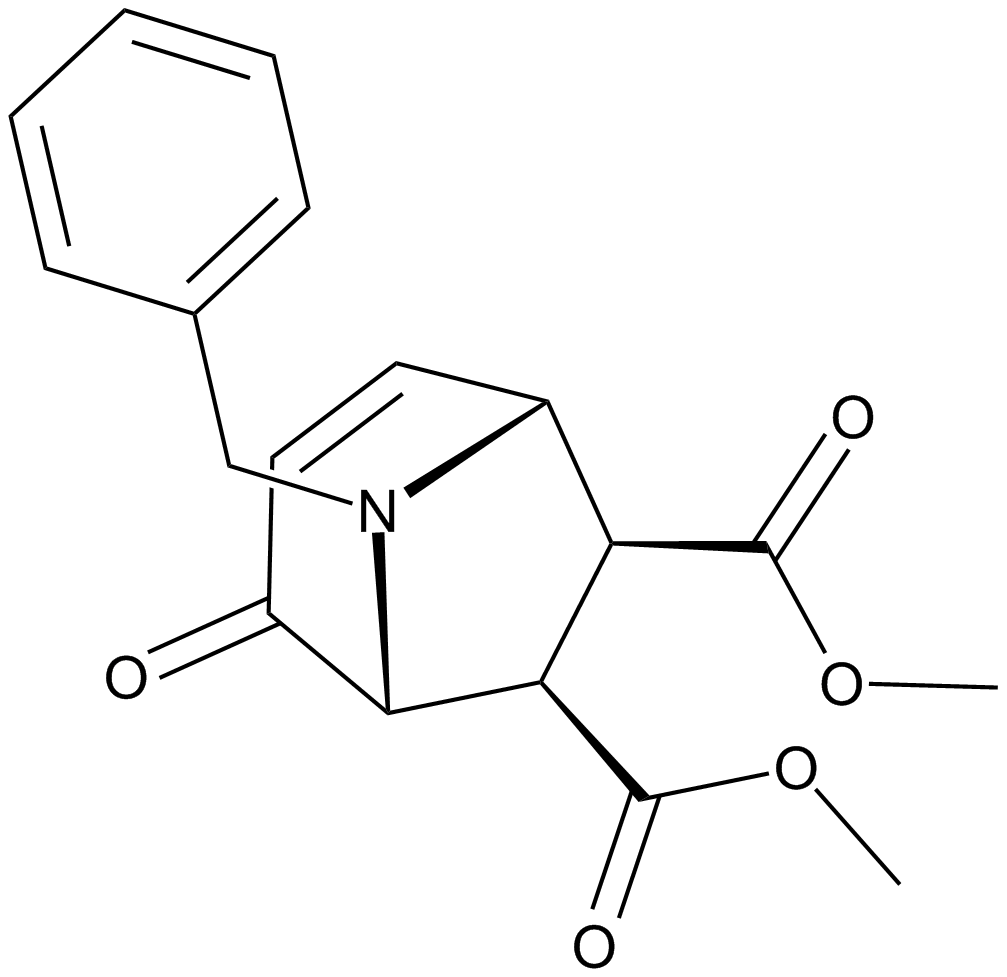 A4515 SD 1008Summary: JAK2/STAT3信号通路抑制剂,细胞凋亡诱导剂
A4515 SD 1008Summary: JAK2/STAT3信号通路抑制剂,细胞凋亡诱导剂 -
 A4513 Lestaurtinib1 CitationSummary: JAK2/FLT3/TrkA抑制剂
A4513 Lestaurtinib1 CitationSummary: JAK2/FLT3/TrkA抑制剂 -
 A4512 Cucurbitacin I中文名: 葫芦素 ITarget: STAT|JAKSummary: STAT3/JAK2信号转导抑制剂
A4512 Cucurbitacin I中文名: 葫芦素 ITarget: STAT|JAKSummary: STAT3/JAK2信号转导抑制剂 -
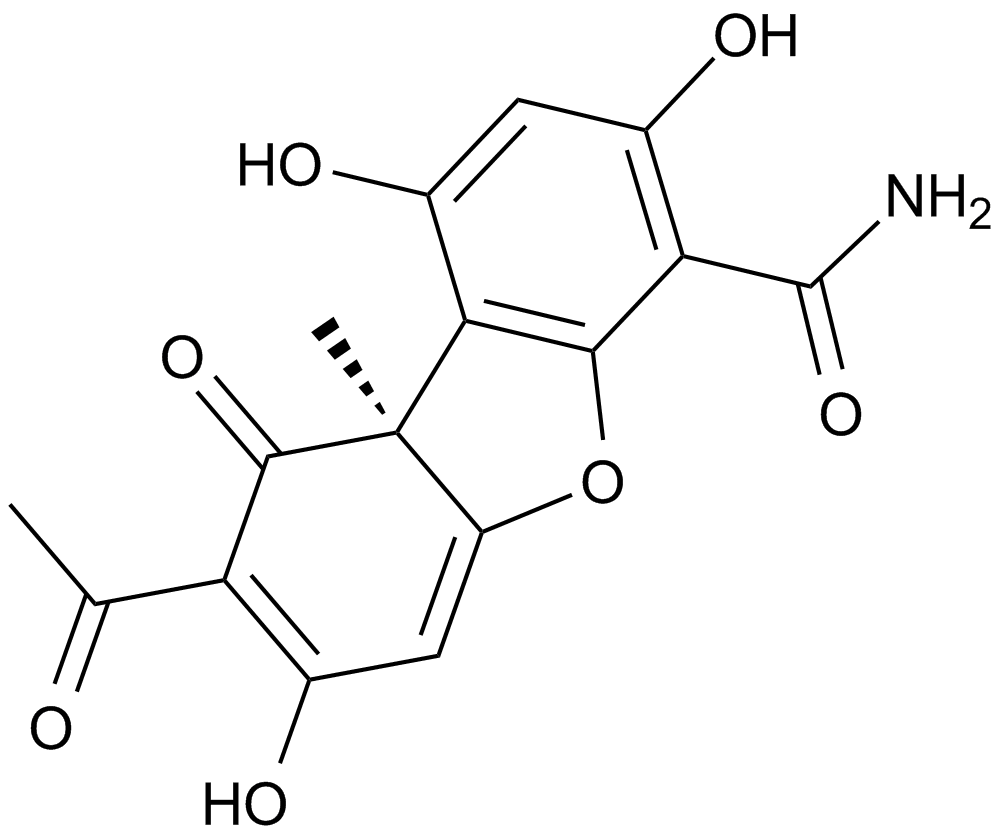 A4511 Cercosporamide中文名: 尾孢素酰胺Target: JAK|MNKSummary: Mnk2和JAK3抑制剂
A4511 Cercosporamide中文名: 尾孢素酰胺Target: JAK|MNKSummary: Mnk2和JAK3抑制剂 -
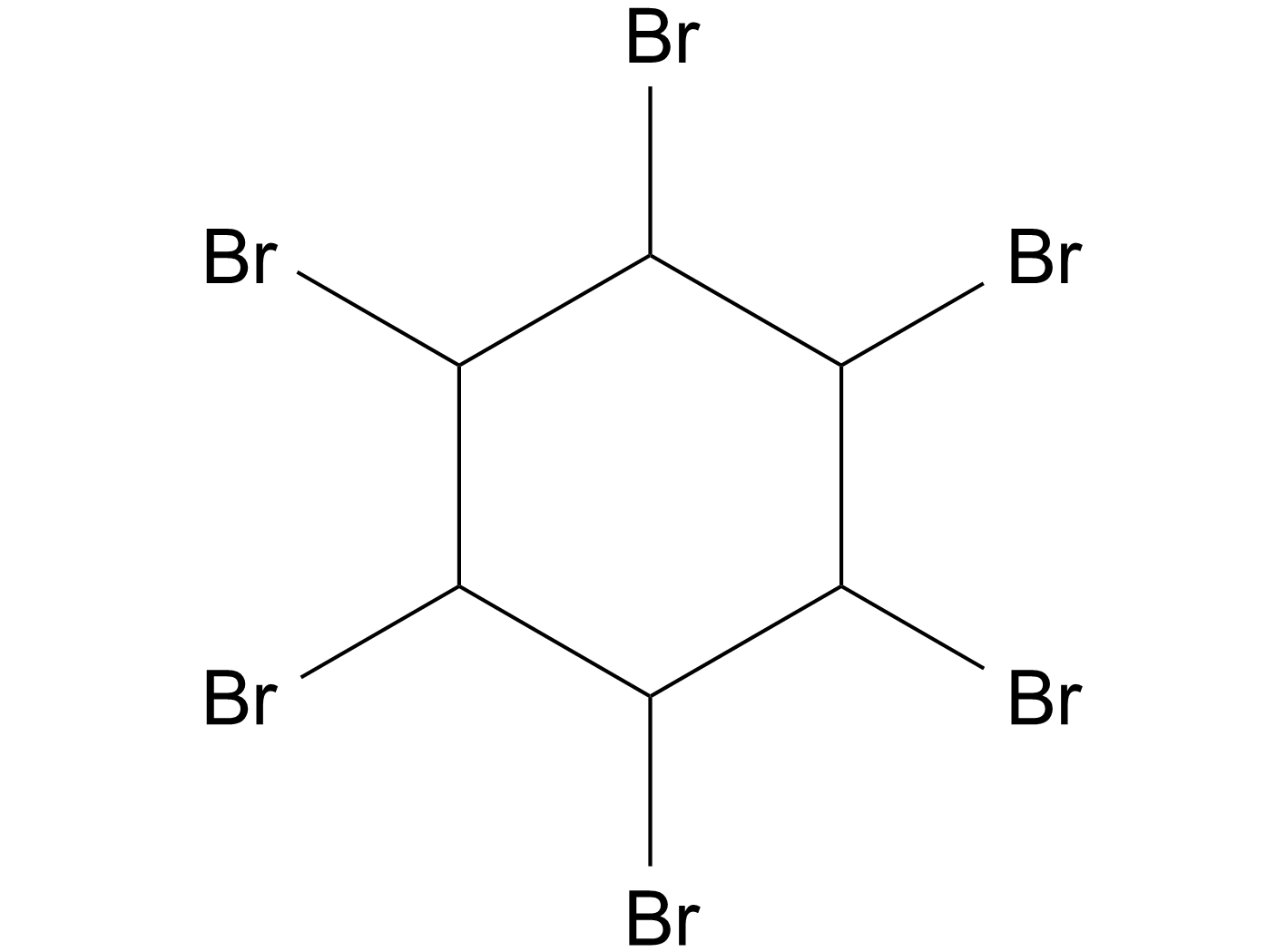 A4510 1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexabromocyclohexane中文名: 六氯环己烷Summary: JAK2酪氨酸激酶抑制剂
A4510 1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexabromocyclohexane中文名: 六氯环己烷Summary: JAK2酪氨酸激酶抑制剂

