Sirtuin
Silent information regulator 2 (Sir2) proteins, also known as sirtuins, are a family of nicotine adenine dinucleotide (NAD) dependent protein deacetylases in organisms ranging from bacteria to humans that are characterized by the presence of a unique and highly conserved catalytic domain of approximately 260 amino acids. Sirtuins are divided into 5 classes, including Class I (subclasses Ia, Ib and Ic), Class II, Class III, Class IV (subclasses IVa and IVb) and Class U (Gram-positive bacteria specific). The catalytic domain of sirtuins is comprised of two bilobed globular domains, the large domain containing the NAD-binding pocket and the small domain binding the acetyl-lysine substrate.
-
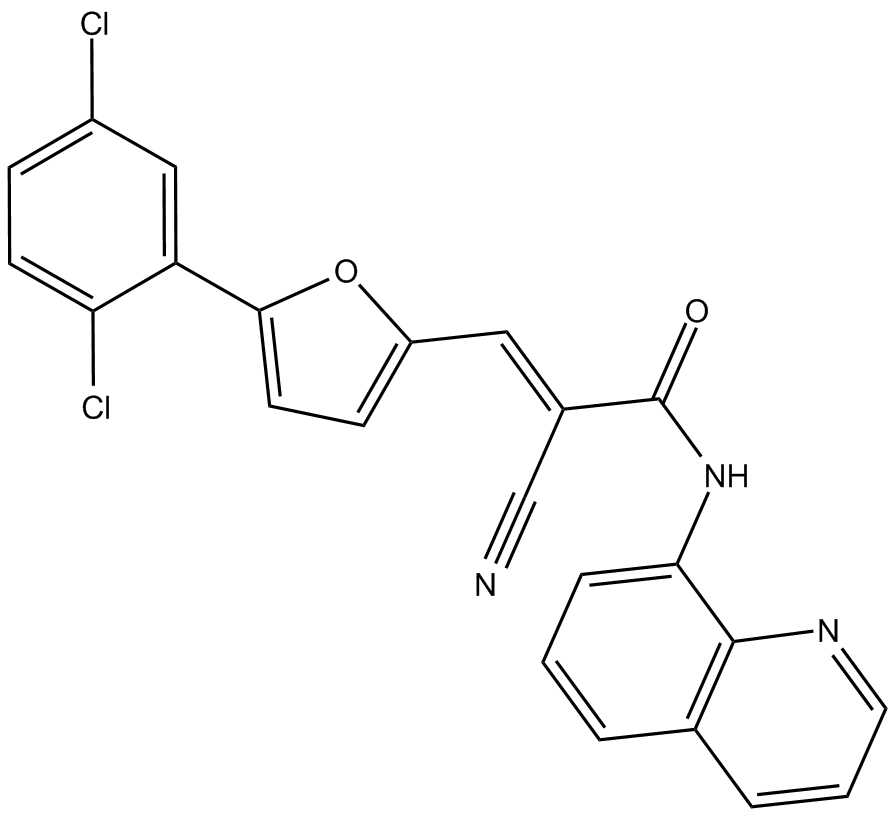 C5709 AGK7Summary: 细胞可渗透的选择性SIRT2抑制剂
C5709 AGK7Summary: 细胞可渗透的选择性SIRT2抑制剂 -
 C5180 JFD00244Summary: SIRT2抑制剂
C5180 JFD00244Summary: SIRT2抑制剂 -
 C3888 JGB1741Summary: SIRT1抑制剂
C3888 JGB1741Summary: SIRT1抑制剂 -
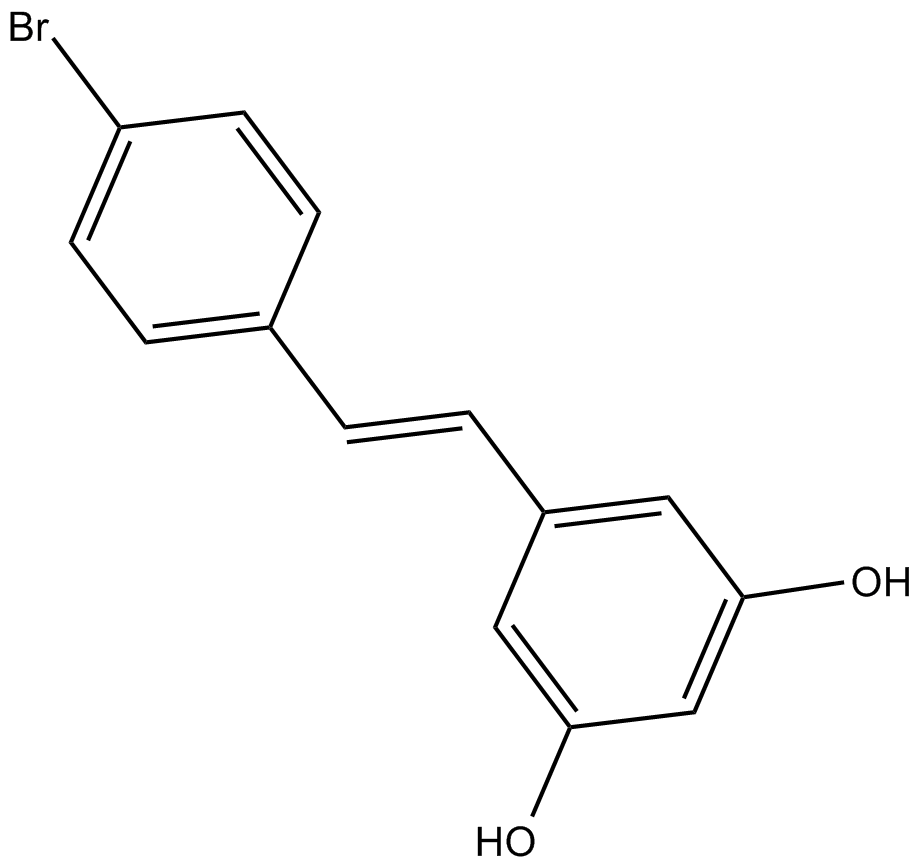 C3552 4'-bromo-Resveratrol1 CitationSummary: Sirt1和Sirt3抑制剂
C3552 4'-bromo-Resveratrol1 CitationSummary: Sirt1和Sirt3抑制剂 -
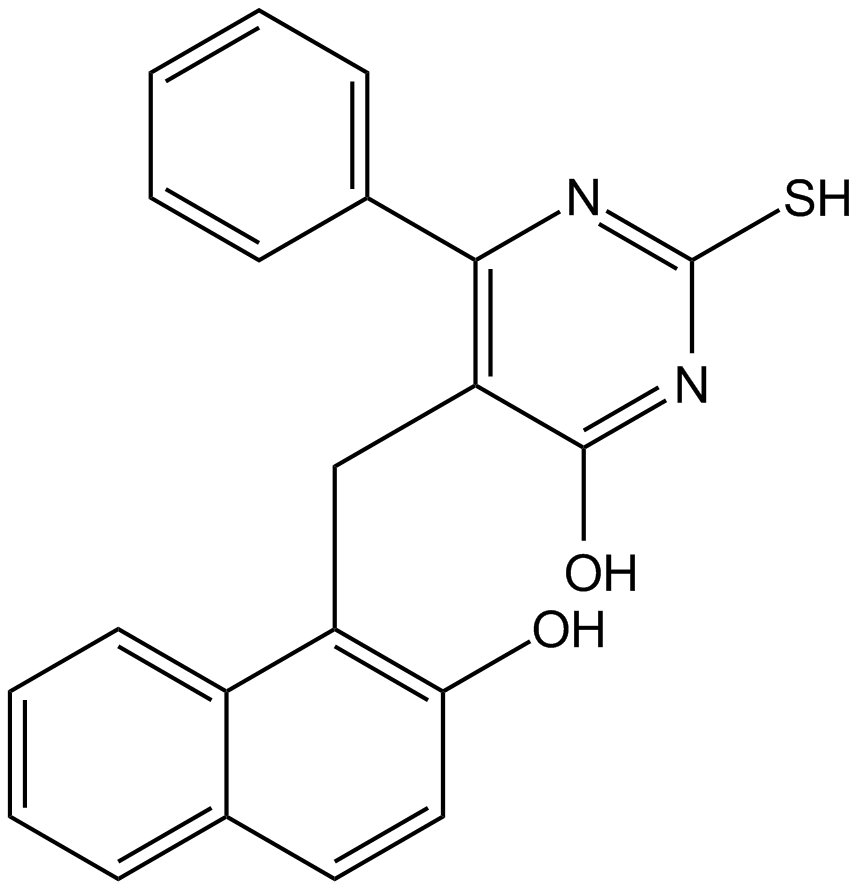 B6063 SIRT1/2 Inhibitor IVSummary: SIRT1和SIRT2抑制剂
B6063 SIRT1/2 Inhibitor IVSummary: SIRT1和SIRT2抑制剂 -
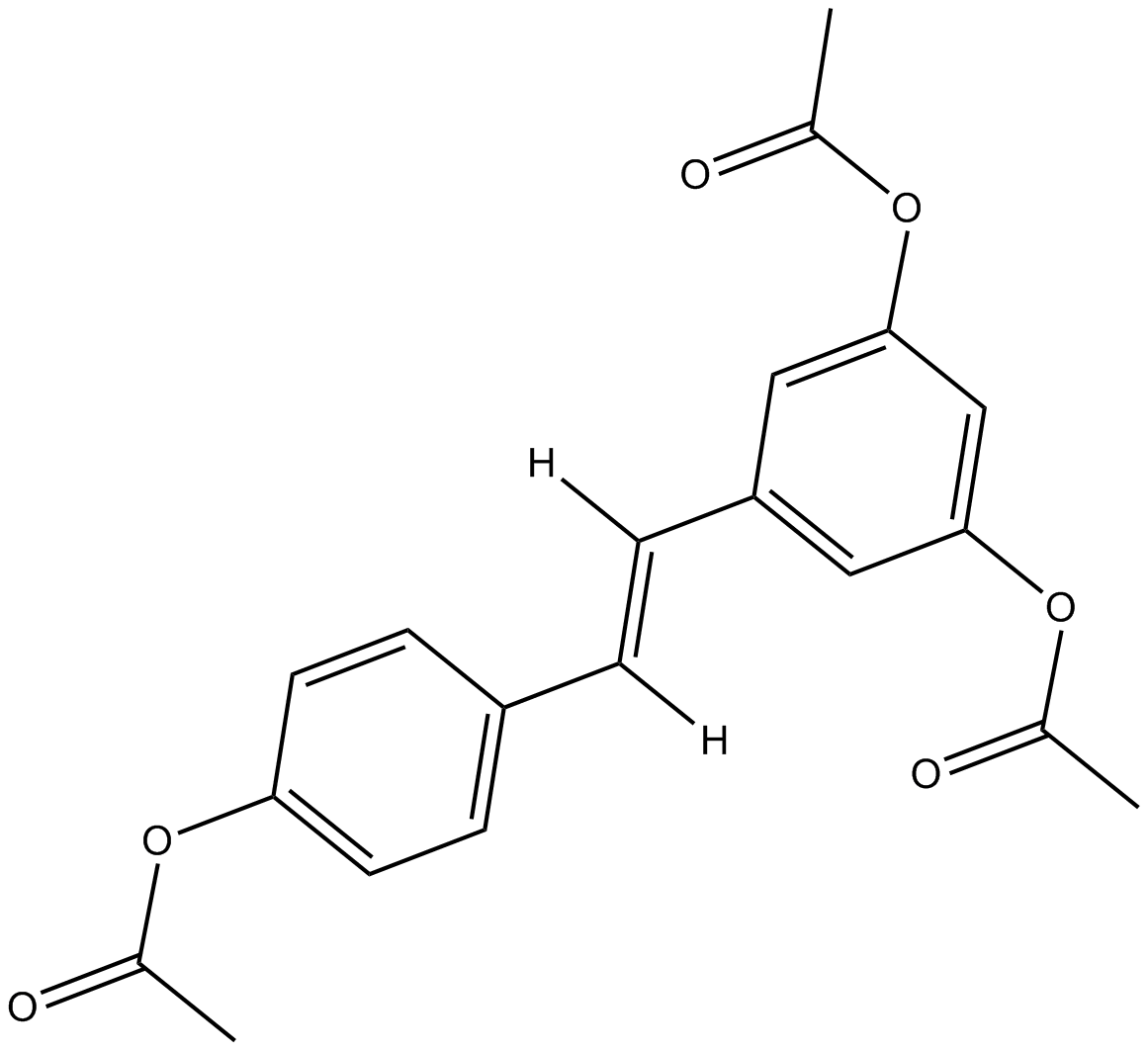 B5971 Triacetyl Resveratrol中文名: 三乙酰基白藜芦醇Summary: 白藜芦醇前药
B5971 Triacetyl Resveratrol中文名: 三乙酰基白藜芦醇Summary: 白藜芦醇前药 -
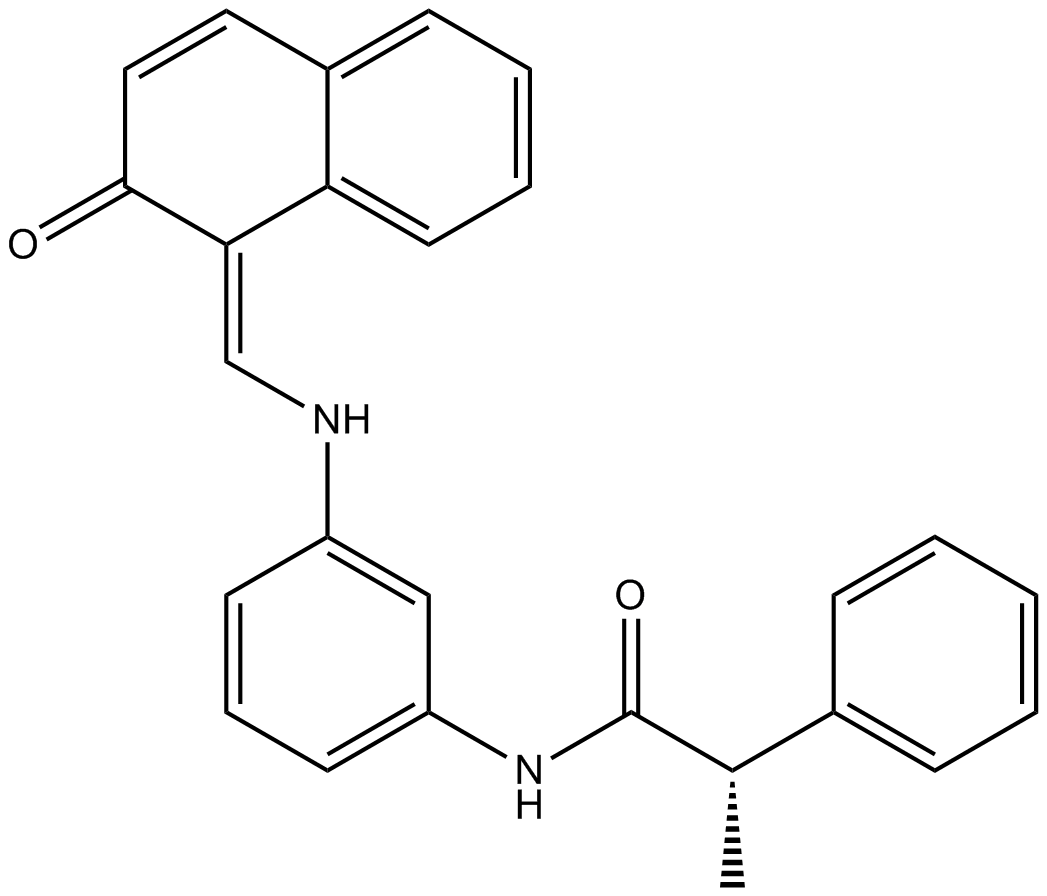 B7594 SalermideSummary: SIRT1和SIRT2抑制剂
B7594 SalermideSummary: SIRT1和SIRT2抑制剂 -
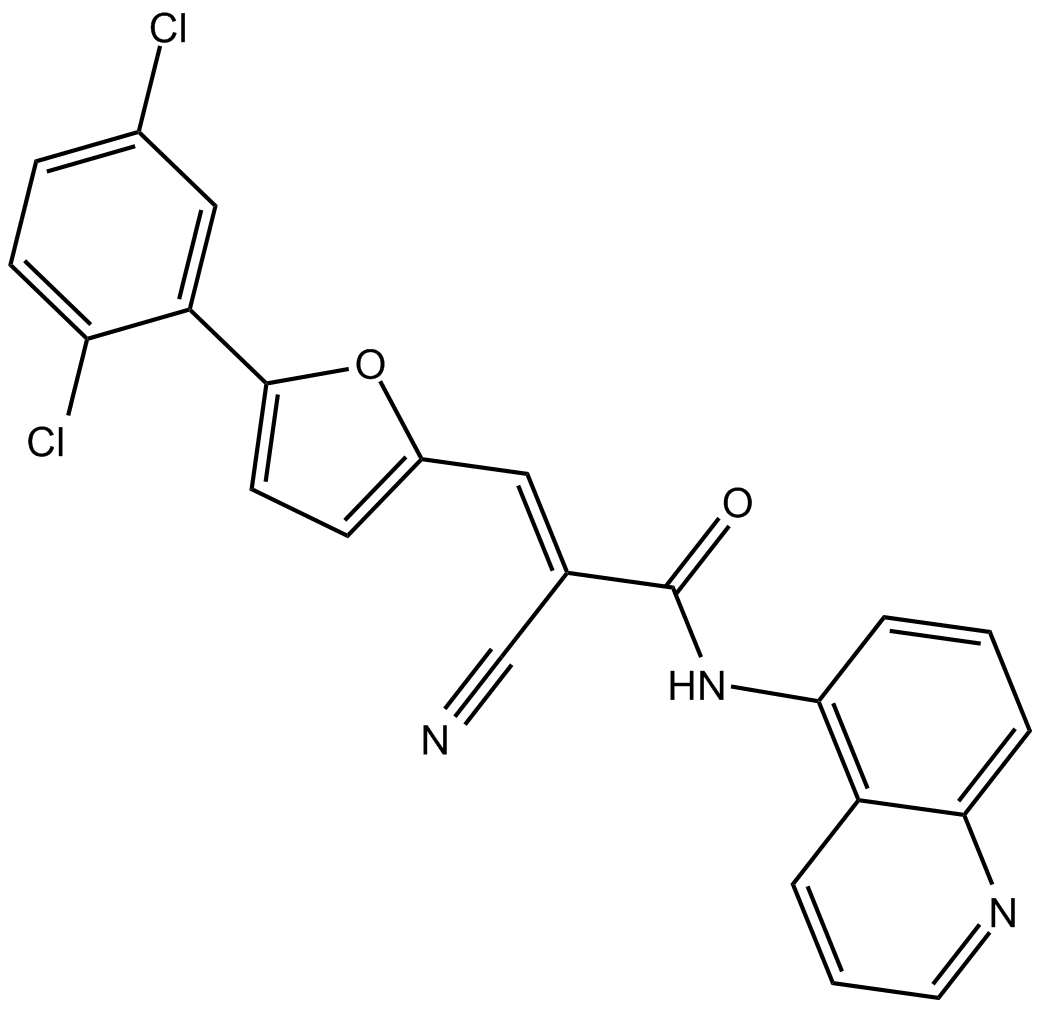 B7323 AGK 2Summary: SIRT2抑制剂
B7323 AGK 2Summary: SIRT2抑制剂 -
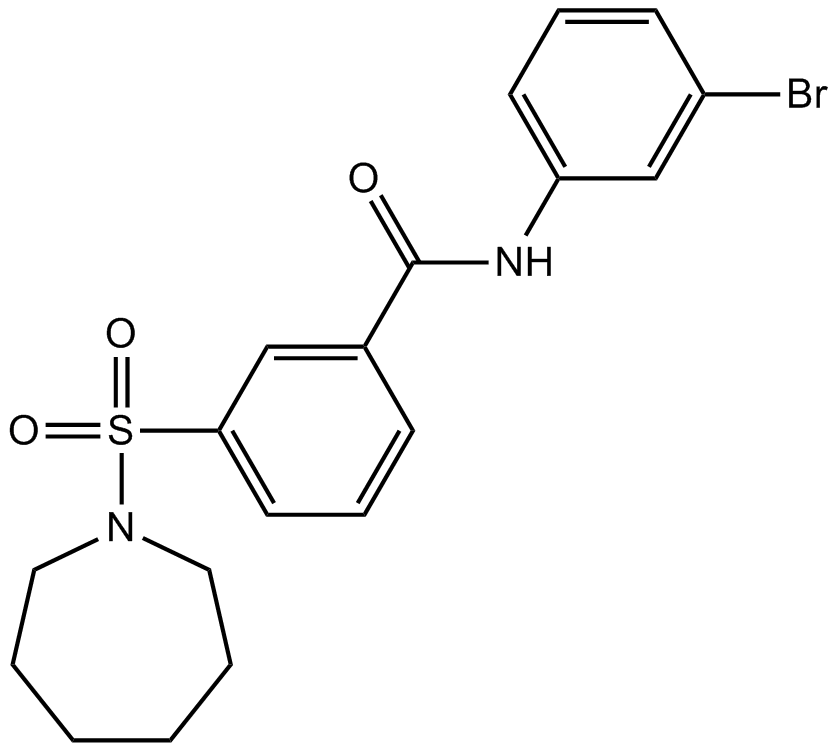 B4713 AK-7Summary: 选择性和脑通透性SIRT2抑制剂
B4713 AK-7Summary: 选择性和脑通透性SIRT2抑制剂 -
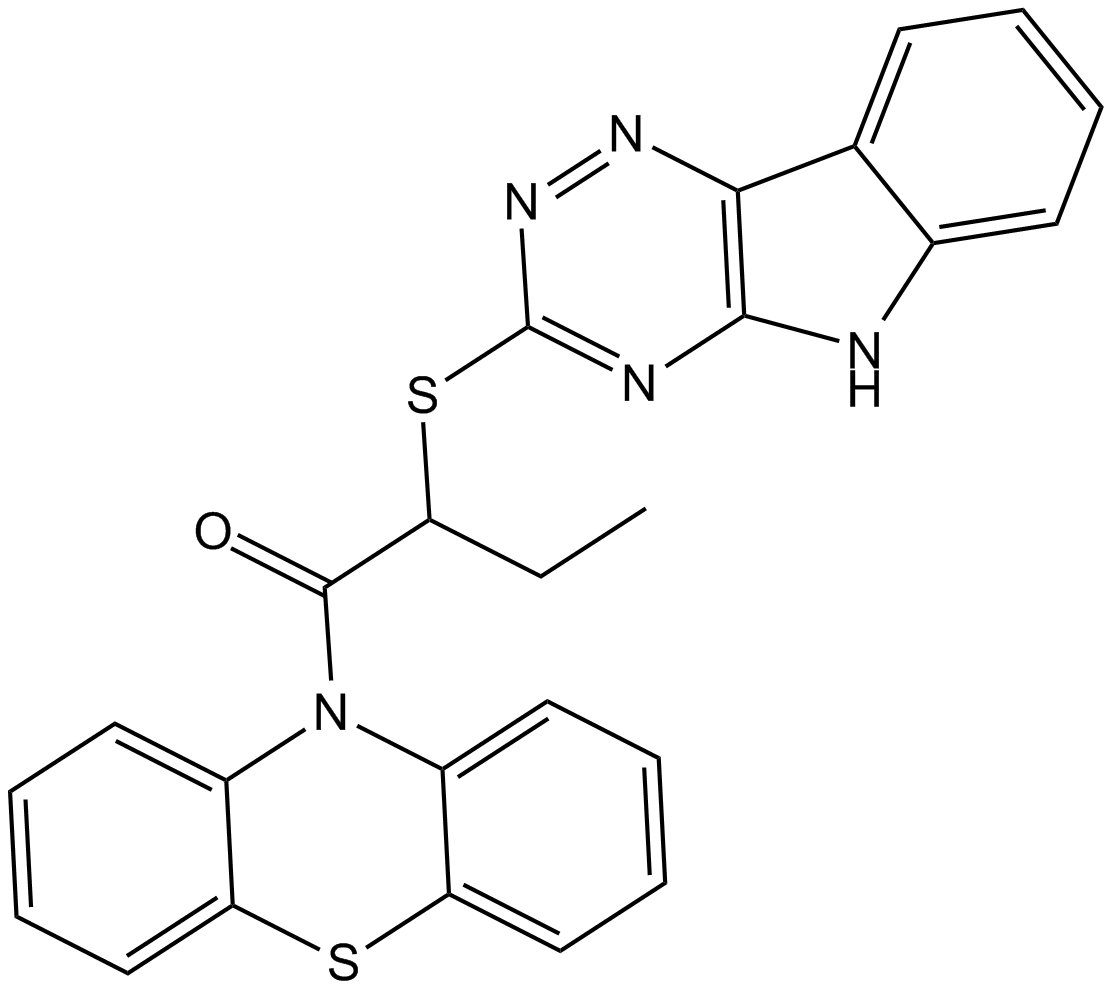 B3272 InauhzinTarget: Sir2-like Family Deacetylases (Sirtuins)Summary: SIRT1抑制剂
B3272 InauhzinTarget: Sir2-like Family Deacetylases (Sirtuins)Summary: SIRT1抑制剂

