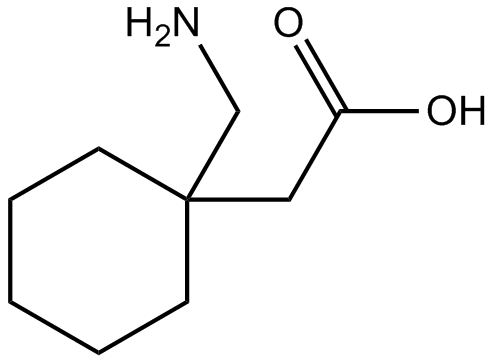
Gabapentin
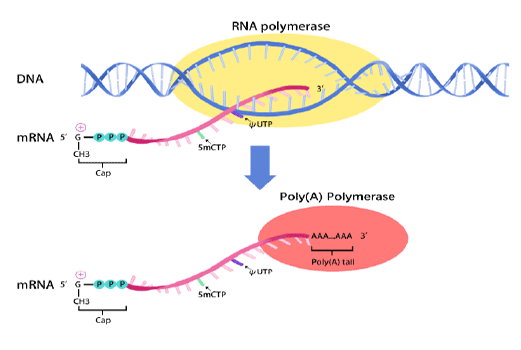
mRNA synthesis
In vitro transcription of capped mRNA with modified nucleotides and Poly(A) tail
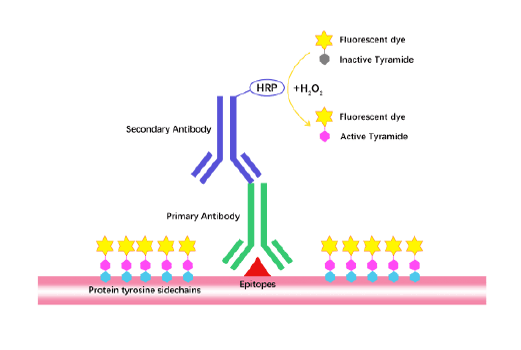
Tyramide Signal Amplification (TSA)
TSA (Tyramide Signal Amplification), used for signal amplification of ISH, IHC and IC etc.
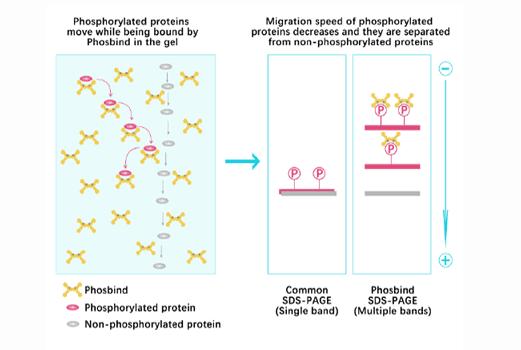
Phos Binding Reagent Acrylamide
Separation of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated proteins without phospho-specific antibody
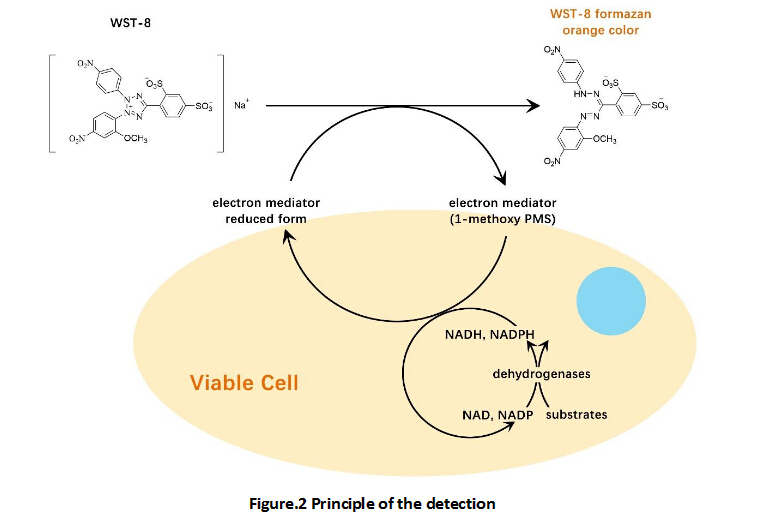
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
A convenient and sensitive way for cell proliferation assay and cytotoxicity assay
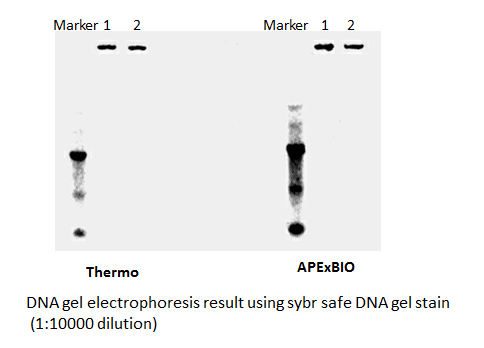
SYBR Safe DNA Gel Stain
Safe and sensitive stain for visualization of DNA or RNA in agarose or acrylamide gels.
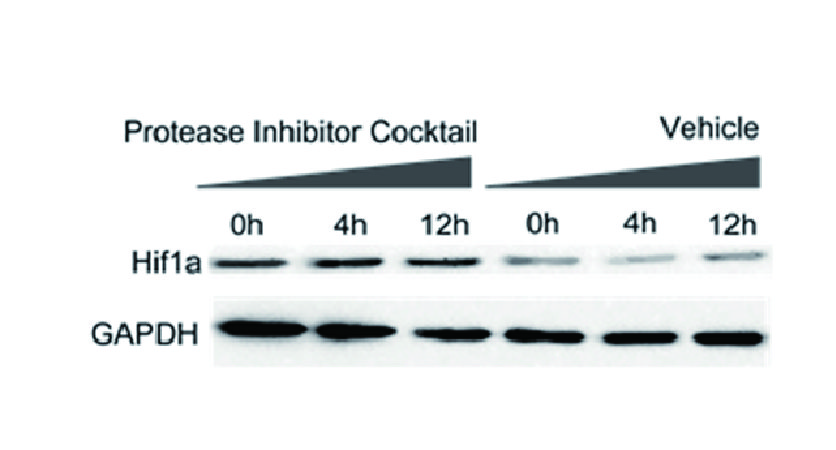
Inhibitor Cocktails
Protect the integrity of proteins from multiple proteases and phosphatases for different applications.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 171.24 |
| Cas No. | 60142-96-3 |
| Formula | C9H17NO2 |
| Solubility | ≥2.6 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥25.85 mg/mL in H2O; insoluble in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | 2-[1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexyl]acetic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | C1CCC(CC1)(CC(=O)O)CN |
| 运输条件 | 蓝冰运输或根据您的需求运输。 |
| 一般建议 | 不同厂家不同批次产品溶解度各有差异,仅做参考。若实验所需浓度过大至产品溶解极限,请添加助溶剂助溶或自行调整浓度。溶液形式一般不宜长期储存,请尽快用完。 |
| 细胞实验[1]: | |
|
细胞系 |
新皮质细胞 |
|
溶解方法 |
溶解度有限。若获取更高浓度的溶液,可在37℃下孵育10分钟,随后在超声波浴中摇匀。-20℃以下可储存数月。 |
|
反应条件 |
10 μM |
|
应用 |
在金字塔新皮质细胞中,Gabapentin抑制高达34%的钙流。在特别低浓度(约10 μM)下,Gabapentin抑制饱和钙电流,在新皮质神经元中的IC 50约4 μM。 |
| 动物实验[1,2]: | |
|
动物模型 |
神经性疼痛动态异常性疼痛大鼠模型,大脑注射溴化乙锭诱发的脑脱髓鞘大鼠模型 |
|
给药剂量 |
口服,10-100 mg/kg |
|
应用 |
在神经性异常性疼痛的大鼠模型中,Gabapentin (10-100 mg/kg, p.o.)以剂量依赖性方式阻断两种类型的异常性疼痛。鞘内注射gabapentin(1-100μg/动物)剂量依赖性阻断静态和动态异常性疼痛。给予后爪类似剂量的gabapentin不能阻止这些反应。在脑内注射(i.c.i)溴化乙锭引起的脑脱髓鞘大鼠模型中,给药300mg/kg gabapentin将皮质MDA增加66%。Gabapentin将GPx活性降低54.3%。100和300 mg/kg剂量的Gabapentin将亚硝酸盐分别降低21.4%和29.2%。Gabapentin增加AChE活性,100和300 mg/kg剂量的Gabapentin分别增加了28.6%和69.3%。100和300 mg/kg剂量的Gabapentin将对氧磷酶活性分别降低了83.3%和73%。 |
|
注意事项 |
由于实验环境的不同,实际溶解度可能与理论值略有不同,请测试室内所有化合物的溶解度。 |
|
References: [1]. Abdel-Salam O M E, Khadrawy Y A, Mohammed N A, et al. The effect of gabapentin on oxidative stress in a model of toxic demyelination in rat brain[J]. 2012. [2]. Field M J, McCleary S, Hughes J, et al. Gabapentin and pregabalin, but not morphine and amitriptyline, block both static and dynamic components of mechanical allodynia induced by streptozocin in the rat[J]. Pain, 1999, 80(1): 391-398. |
|
质量控制和MSDS
- 批次:
化学结构