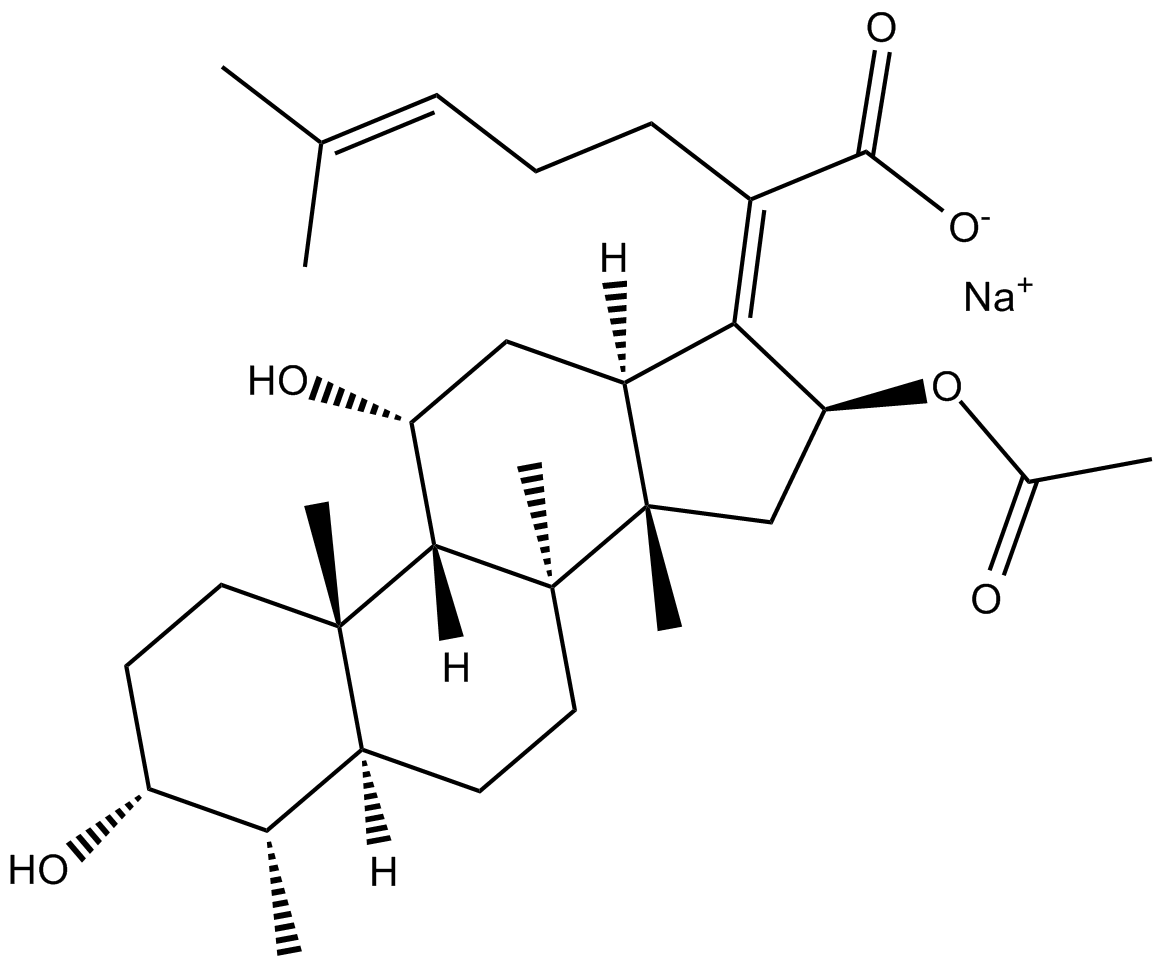
Fusidic Acid (sodium salt)
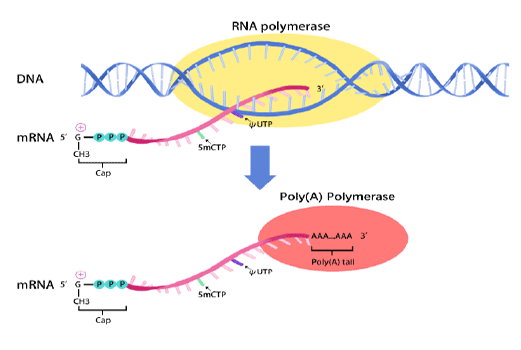
mRNA synthesis
In vitro transcription of capped mRNA with modified nucleotides and Poly(A) tail
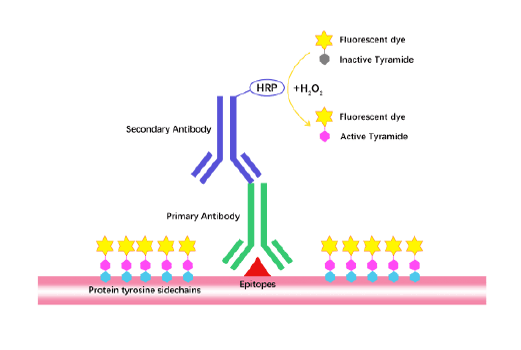
Tyramide Signal Amplification (TSA)
TSA (Tyramide Signal Amplification), used for signal amplification of ISH, IHC and IC etc.
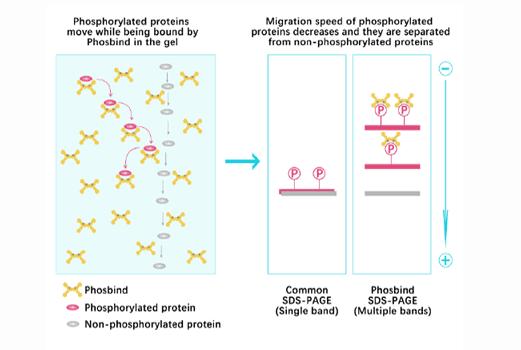
Phos Binding Reagent Acrylamide
Separation of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated proteins without phospho-specific antibody
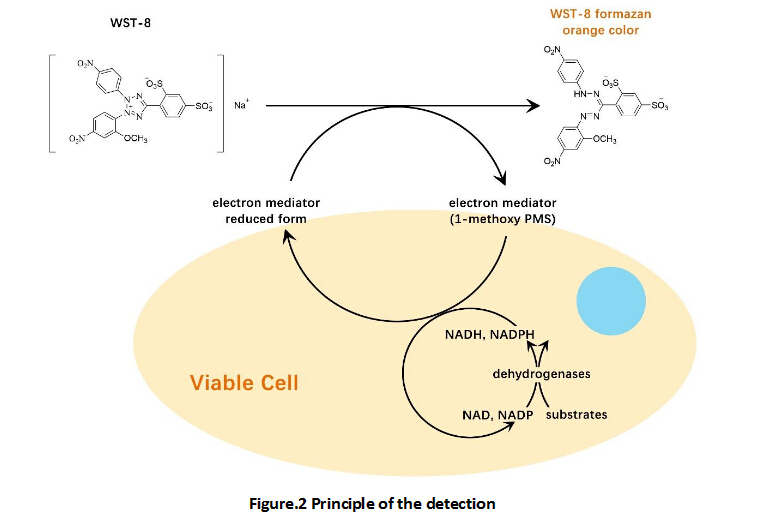
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
A convenient and sensitive way for cell proliferation assay and cytotoxicity assay
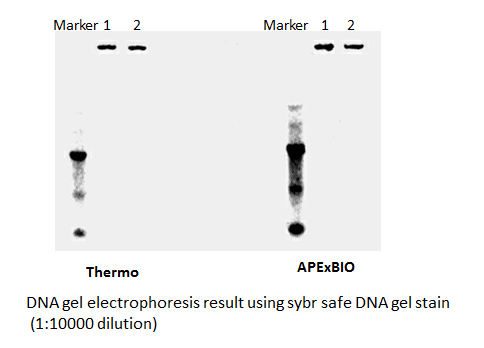
SYBR Safe DNA Gel Stain
Safe and sensitive stain for visualization of DNA or RNA in agarose or acrylamide gels.
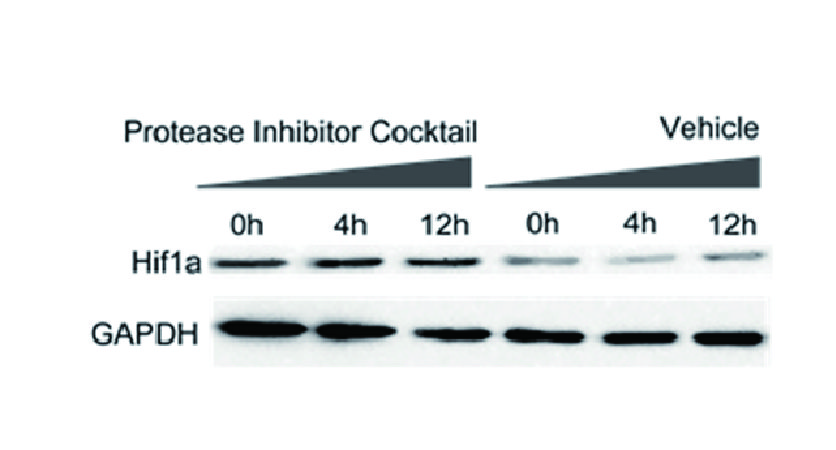
Inhibitor Cocktails
Protect the integrity of proteins from multiple proteases and phosphatases for different applications.
IC50: ~10-200 μM for the translocation function of the elongation factor EF-G
Fusidic acid is a steroidal antibiotic.
Fusidic acid was identified as a steroidal antibiotic produced by the fungus Fusidium conccineum.
In vitro: Resistance to fusidic acid in S. aureus strains was selected and mutations were identified in the fusA gene, which encodes EF-G. Fusidic acid could not bind to free EF-G, but rather to EF-G GTP in the complex with ribosome, suggesting that the antibiotic required a specific conformation of EF-G for binding. Biochemically, fusidic acid permited ribosome-stimulated GTP hydrolysis by EF-G, but prevented the associated conformational changes in EF-G, and therefore prevented EF-G turnover by stabilizing EF-G GDP on the ribosome. Fusidic acid did not work on eukaryotes, but sordarin was considered to similarly act on yeast EF2 and was used to assemble EF2-80S yeast ribosome complexes for cryo-EM analysis [1].
In vivo: Animal study found that fusidic acid sodium salt was well absorbed after oral administration and it could significantly reduce the diabetes incidence in BB rats. Fusidic acid sodium salt substantially accumulated more in female rats which might refult from the steroid structure of fusidin [2].
Clinical trial: Fusidic acid was first introduced into clinical use in 1962 mainly for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections [1].
References:
[1] Wilson, D. N. The A-Z of bacterial translation inhibitors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 44(6), 393-433 (2009).
[2] Hageman I, Buschard K. Antidiabetogenic effect of fusidic acid in diabetes prone BB rats: a sex-dependent organ accumulation of the drug is seen. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002 Sep;91(3):123-8.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 538.7 |
| Cas No. | 751-94-0 |
| Formula | C31H47O6·Na |
| Synonyms | SQ 16,360 |
| Solubility | ≥14.15 mg/mL in H2O; ≥31.7 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥52.4 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | (4α,8α,9β,13α,14β)-16β-(acetyloxy)- 3α,11α-dihydroxy-29-nordammara-17Z(20),24-dien-21-oic acid, monosodium salt |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(C)[C@](CC[C@@]3(C)[C@@]2([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]4([H])[C@]3(C)C[C@H](OC(C)=O)/C4=C(C([O-])=O)/CC/C=C(C)/C)([H])[C@@H]1C.[Na+] |
| 运输条件 | 蓝冰运输或根据您的需求运输。 |
| 一般建议 | 不同厂家不同批次产品溶解度各有差异,仅做参考。若实验所需浓度过大至产品溶解极限,请添加助溶剂助溶或自行调整浓度。溶液形式一般不宜长期储存,请尽快用完。 |
| 动物实验 [1]: | |
|
动物模型 |
糖尿病易发性BB大鼠 |
|
剂量 |
339mg/天(雄性大鼠)和245 mg/天(雌性大鼠),食物中添加fusidin;200mg/天(雄性大鼠)和 163 mg/天(雌性大鼠),饮用水中添加fusidin。 |
|
应用 |
动物研究发现,fusidic acid sodium salt 口服后吸收良好,可以显着降低BB大鼠的糖尿病发病率。 Fusidic acid sodium salt 在雌性大鼠中大量积累,可能是从fusidin的类固醇结构中产生的。 |
|
注意事项 |
请测试所有化合物在室内的溶解度,实际溶解度和理论值可能略有不同,这是由实验系统的误差引起的,属于正常现象。 |
|
References: [1]. Hageman I, Buschard K. Antidiabetogenic effect of fusidic acid in diabetes prone BB rats: a sex-dependent organ accumulation of the drug is seen. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002 Sep;91(3):123-8. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0773.2002.910306.x. PMID: 12427112. |
|
质量控制和MSDS
- 批次:
化学结构