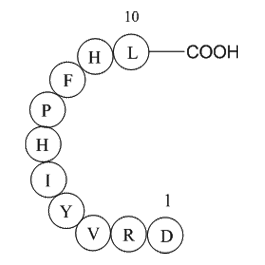
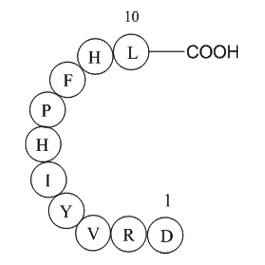
Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat)
mRNA synthesis
In vitro transcription of capped mRNA with modified nucleotides and Poly(A) tail
Tyramide Signal Amplification (TSA)
TSA (Tyramide Signal Amplification), used for signal amplification of ISH, IHC and IC etc.
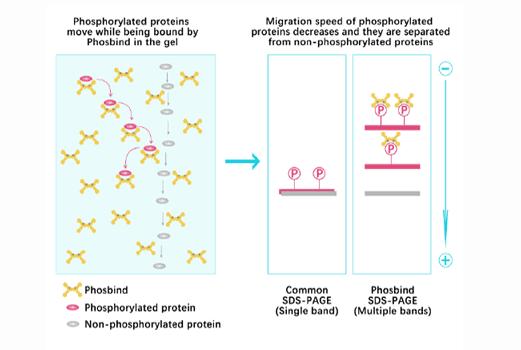
Phos Binding Reagent Acrylamide
Separation of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated proteins without phospho-specific antibody
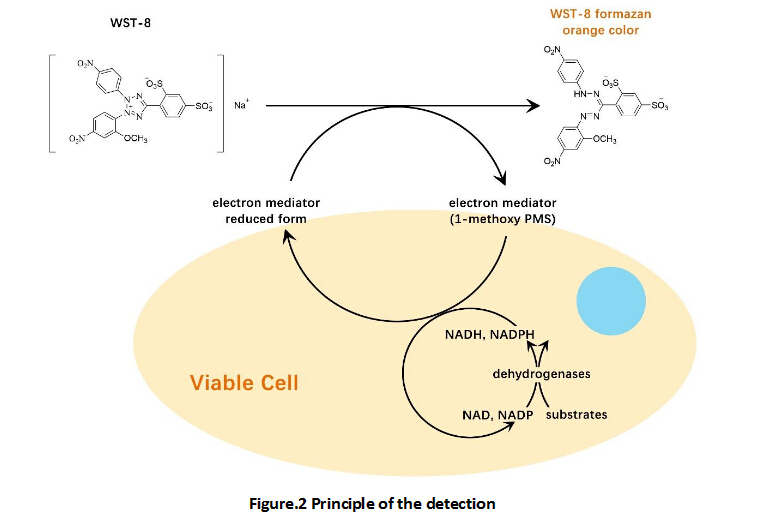
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
A convenient and sensitive way for cell proliferation assay and cytotoxicity assay
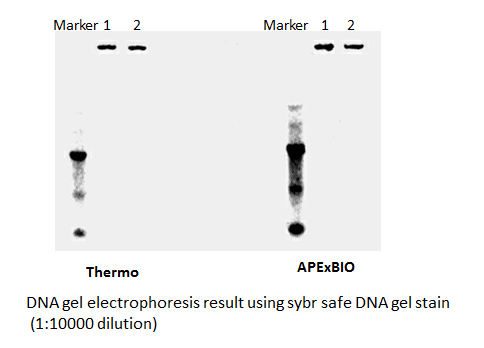
SYBR Safe DNA Gel Stain
Safe and sensitive stain for visualization of DNA or RNA in agarose or acrylamide gels.
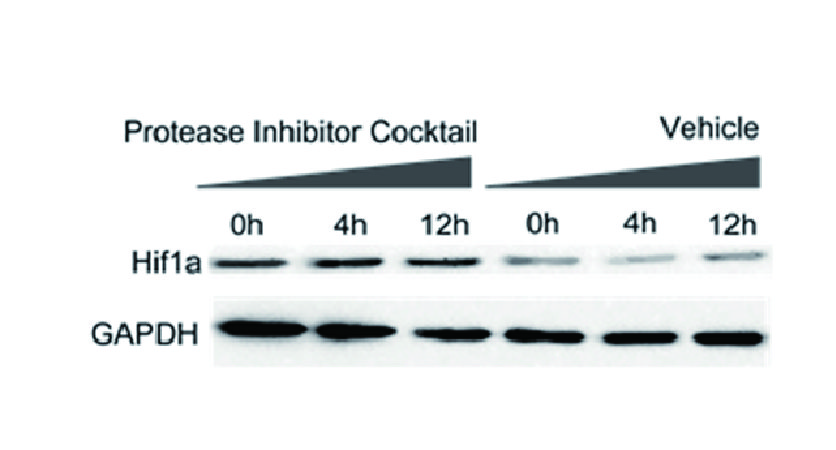
Inhibitor Cocktails
Protect the integrity of proteins from multiple proteases and phosphatases for different applications.
血管紧张素I(Ang I)化学式为C62H89N17O14,多肽序列为H-Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe-His-Leu-OH ,是通过肾素对血管紧张素的作用形成的。肾素在肾脏中产生,肾脏响应肾交感神经活动,减少肾小球旁细胞中肾内血压(收缩压小于90mmHg),从而产生肾素。Ang I似乎没有生物活性,仅仅是作为血管紧张素II(AII)的前体物质。在血管紧张素转换酶(ACE)作用下,血管紧张素I转变为血管紧张素Ⅱ。在血管平滑肌细胞中,血管紧张素Ⅱ通过刺激Gq蛋白增加血压,最终通过IP3依赖机制激活血管收缩。
参考文献:
1. Lundequist, A. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 32339 (2004); Olson, S. et al. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell Mol. Physiol. 287, L559 (2004); Sanker, S. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 2963 (1997).
2. Preston RA, Materson BJ, Reda DJ, et al. Age-Race Subgroup Compared With Renin Profile as Predictors of Blood Pressure Response to Antihypertensive Therapy. JAMA. 1998;280(13):1168-1172. doi:10.1001/jama.280.13.1168.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1296.5 |
| Cas No. | 484-42-4 |
| Formula | C62H89N17O14 |
| Synonyms | Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe-His-Leu |
| Solubility | ≥129.6 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥124.2 mg/mL in H2O; ≥9.16 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CC1=CN=CN1)C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)NC(CC3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)NC(CC4=CN=CN4)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC5=CC=C(C=C5)O)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)N |
| 运输条件 | 蓝冰运输或根据您的需求运输。 |
| 一般建议 | 不同厂家不同批次产品溶解度各有差异,仅做参考。若实验所需浓度过大至产品溶解极限,请添加助溶剂助溶或自行调整浓度。溶液形式一般不宜长期储存,请尽快用完。 |
| Animal experiment:[1] | |
|
Animal models |
Time-dated pregnant ewes (gestational day 125 ± 5, term ~ 145 days) |
|
Dosage form |
5 μg/kg Intracerebroventricular injection |
|
Applications |
Intracerebroventricular injection of Ang I significantly increased fetal blood pressure and c-fos expression in the supraoptic nuclei (SON) and the paraventricular nuclei (PVN) in the hypothalamus, accompanied by an increase of fetal plasma arginine vasopressin (AVP). Double labeling experiments showed colocalization of AT1 receptor and c-fos expression in both SON and PVN following Ang I treatment. The results indicate that central angiotensin I increases fetal AVP neuron activity and pressor responses. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Shi L, Mao C, Zeng F, et al. Central angiotensin I increases fetal AVP neuron activity and pressor responses. American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2010, 298(6): E1274-1282. |
|
质量控制和MSDS
- 批次:
化学结构