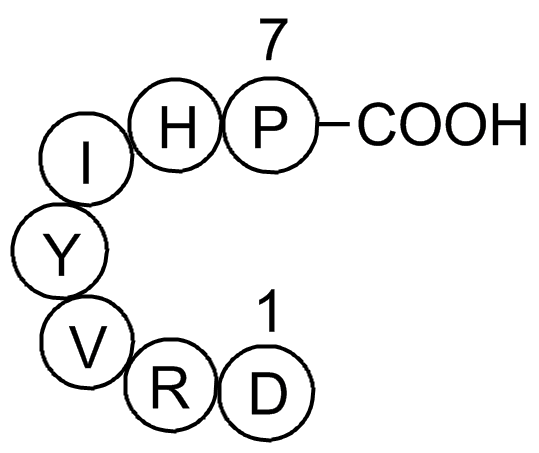
Angiotensin (1-7)
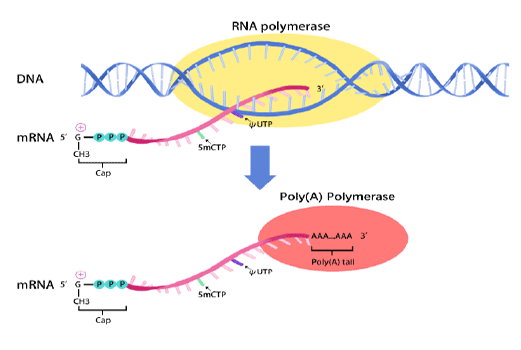
mRNA synthesis
In vitro transcription of capped mRNA with modified nucleotides and Poly(A) tail
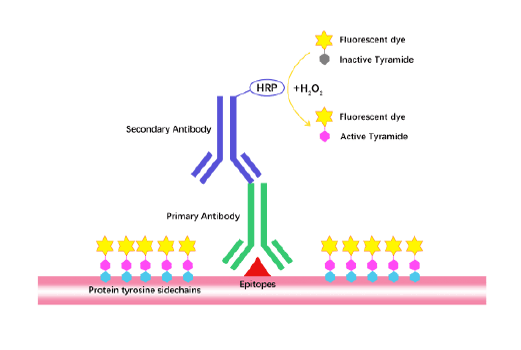
Tyramide Signal Amplification (TSA)
TSA (Tyramide Signal Amplification), used for signal amplification of ISH, IHC and IC etc.
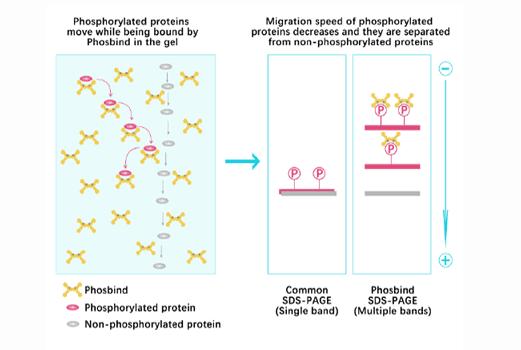
Phos Binding Reagent Acrylamide
Separation of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated proteins without phospho-specific antibody
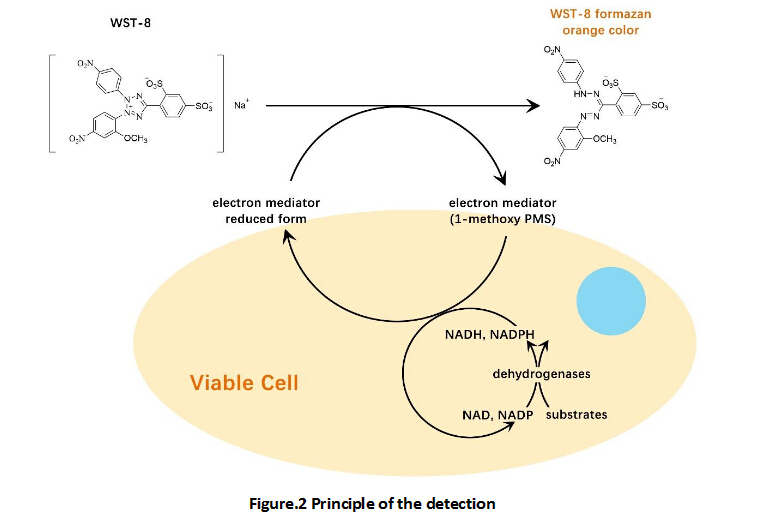
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
A convenient and sensitive way for cell proliferation assay and cytotoxicity assay
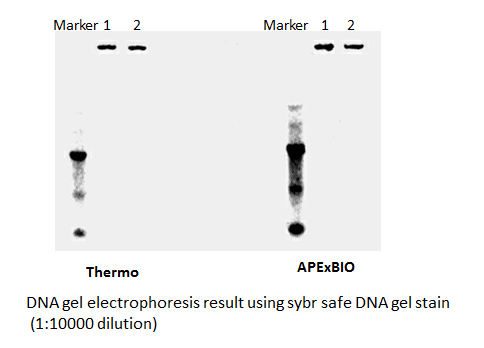
SYBR Safe DNA Gel Stain
Safe and sensitive stain for visualization of DNA or RNA in agarose or acrylamide gels.
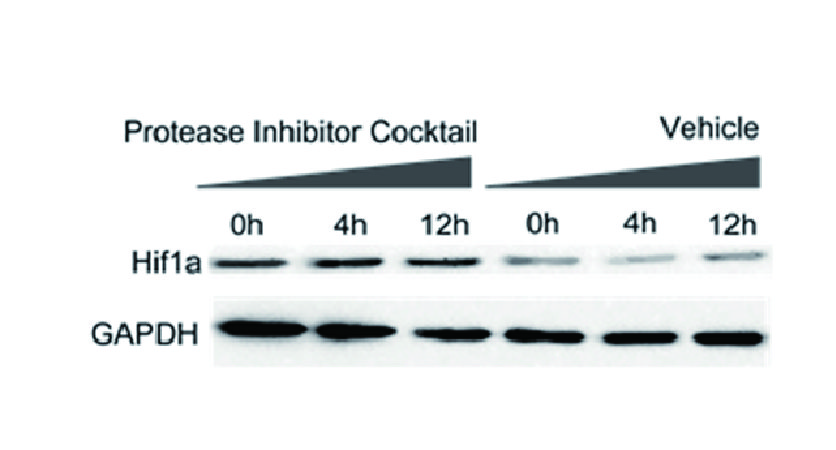
Inhibitor Cocktails
Protect the integrity of proteins from multiple proteases and phosphatases for different applications.
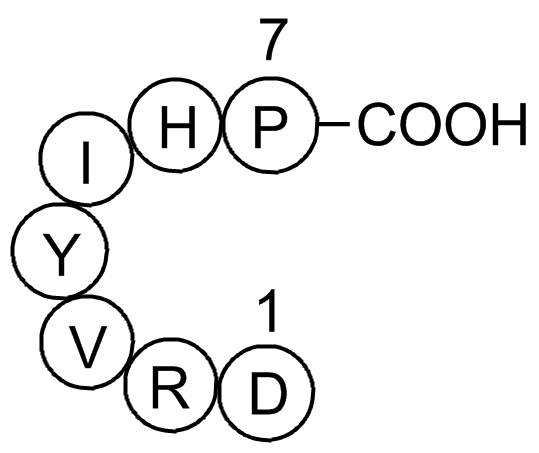
Ang(1-7)的氨基酸序列为H - Asp - Arg - Val - Tyr - Ile - His - Pro – OH,是血管紧张素I或血管紧张素Ⅱ在内肽酶或羧基肽酶作用下产生的内源性肽片段[1]。
最初发现的Ang(1-7)主要在心血管和肾脏中发挥功能,Ang(1-7)与血管紧张素Ⅱ类似,在不同器官和组织广泛分布,发挥作用。这些作用是由Mas介导的,可以反向调节血管紧张素Ⅱ造成的大部分有害影响。Ang(1-7)/Mas的相互作用调节不同的信号通路,如PI3K(磷酸肌醇3-激酶)/AKT和ERK(胞外信号调节激酶)途径,下游效应因子如NO、FOXO1和COX-2(环氧化酶-2)参与其中。通过这些机制,Ang(1-7)能够改善一些病理状况,包括器官的纤维化和炎症,如肺、肝和肾脏[2]。
此外,这种七肽对代谢具有积极的效果,增加葡萄糖摄取和脂肪分解,同时降低胰岛素抗性和血脂异常。除了影响学习和记忆外,在缺血性中风中,Angiotensin (1-7)能够提高脑保护。Ang(1-7)可以作用于生殖系统,具有增强排卵以及精子和类固醇合成的作用。Ang(1-7) 能够抑制细胞增殖和血管生成,被认为是一种潜在的抗癌治疗手段[2]。
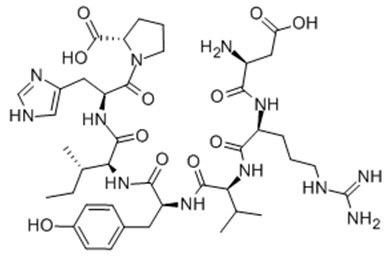
Fig. 1: Formula of Angiotensin (1-7)
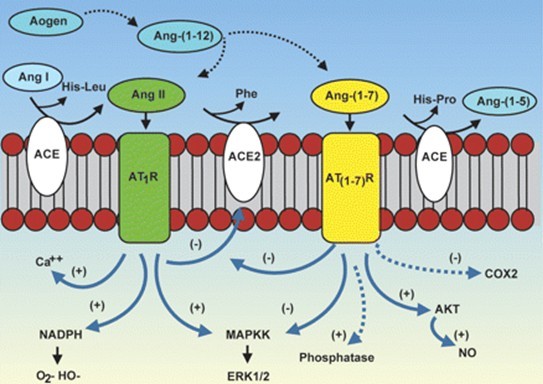
Fig. 2: Cascade of the processing of angiotensin peptides and their interaction with AT1 and AT1-7 receptor systems.
参考文献:
1. Santos et al (2000) Angiotensin-(1-7): an update. Regul.Pept. 91 45.
2. Danielle G. P., Thiago V., Robson A. S. Angiotensin-(1-7): beyond the cardio-renal actions. Clinical Science (2013) 124, (443–456)
- 1. Ying Li, Jiao Song, et al. "Ang-(1-7) Protects Skeletal Muscle Function in Aged Mice." BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Sep 21;22(1):809. PMID: 34548056
- 2. Sanket Patel, Tahir Hussain, et al. "Synergism between Angiotensin receptors ligands: Role of Angiotensin‐(1‐7) in modulating AT2R agonist response on nitric oxide in kidney cells." Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020 Dec;8(6):e00667. PMID: 33197136
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 899 |
| Cas No. | 51833-78-4 |
| Formula | C41H62N12O11 |
| Synonyms | Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; ≥48.5 mg/mL in H2O; ≥89.9 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | Angiotensin (1-7) |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CC1=CN=CN1)C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC3=CC=C(C=C3)O)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)N |
| 运输条件 | 蓝冰运输或根据您的需求运输。 |
| 一般建议 | 不同厂家不同批次产品溶解度各有差异,仅做参考。若实验所需浓度过大至产品溶解极限,请添加助溶剂助溶或自行调整浓度。溶液形式一般不宜长期储存,请尽快用完。 |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Rat kidney NRK-52E cells |
|
Reaction Conditions |
100 nM angiotensin (1-7) |
|
Applications |
Angiotensin (1-7) abrogated the methylglyoxal albumin-stimulated myofibroblast phenotype by inhibiting the chronic stimulation of the TGF-β-ERK pathway in NRK-52E cells. Moreover, the inhibitory effects of angiotensin (1-7) on myofibroblast transition could be reversed by the angiotensin (1-7) receptor antagonist A779 (10 μM). |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
Male and female BALB/c mice (1:1 ratio, 6 ~ 10 weeks old, mean weight 20 g) |
|
Dosage form |
0.01, 0.06, 0.1, 0.3 and 1 mg/kg Once daily by intraperitoneal route |
|
Applications |
Daily angiotensin (1-7) treatment (0.01 ~ 0.06 mg/kg) resulted in significant amelioration of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis, whereas daily administration of A779 significantly worsened features of colitis. Colitis-associated phosphorylation of p38, ERK1/2 and Akt was also reduced by angiotensin (1-7) treatment. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Alzayadneh EM, Chappell MC. Angiotensin-(1-7) abolishes AGE-induced cellular hypertrophy and myofibroblast transformation via inhibition of ERK1/2. Cellular Signalling, 2014, 26(12): 3027-3035. 2. Khajah MA, Fateel MM, Ananthalakshmi KV, et al. Anti-inflammatory action of angiotensin 1-7 in experimental colitis. PLoS One, 2016, 11(3): e0150861. |
|
质量控制和MSDS
- 批次:
化学结构
相关生物数据